Execute SQL Commands and Create Custom Notifications with SAP Automation Pilot and SAP Alert Notification Service
- How to create a command in SAP Automation Pilot which connects to and queries an SAP HANA Cloud database instance
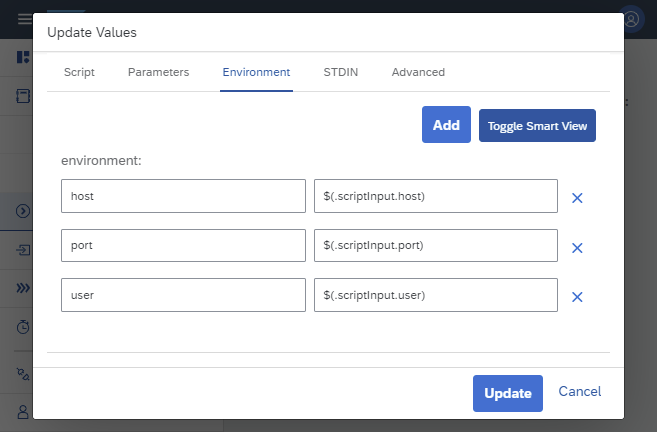
- How to perform queries using the provided
ExecuteHanaCloudSqlStatement - How to perform queries using
hdbcli, the SAP HANA client driver for Python - How to conditionally send a notification (email) with the results of the query using the SAP Alert Notification Service
- How to schedule an SAP Automation Pilot command
Prerequisites
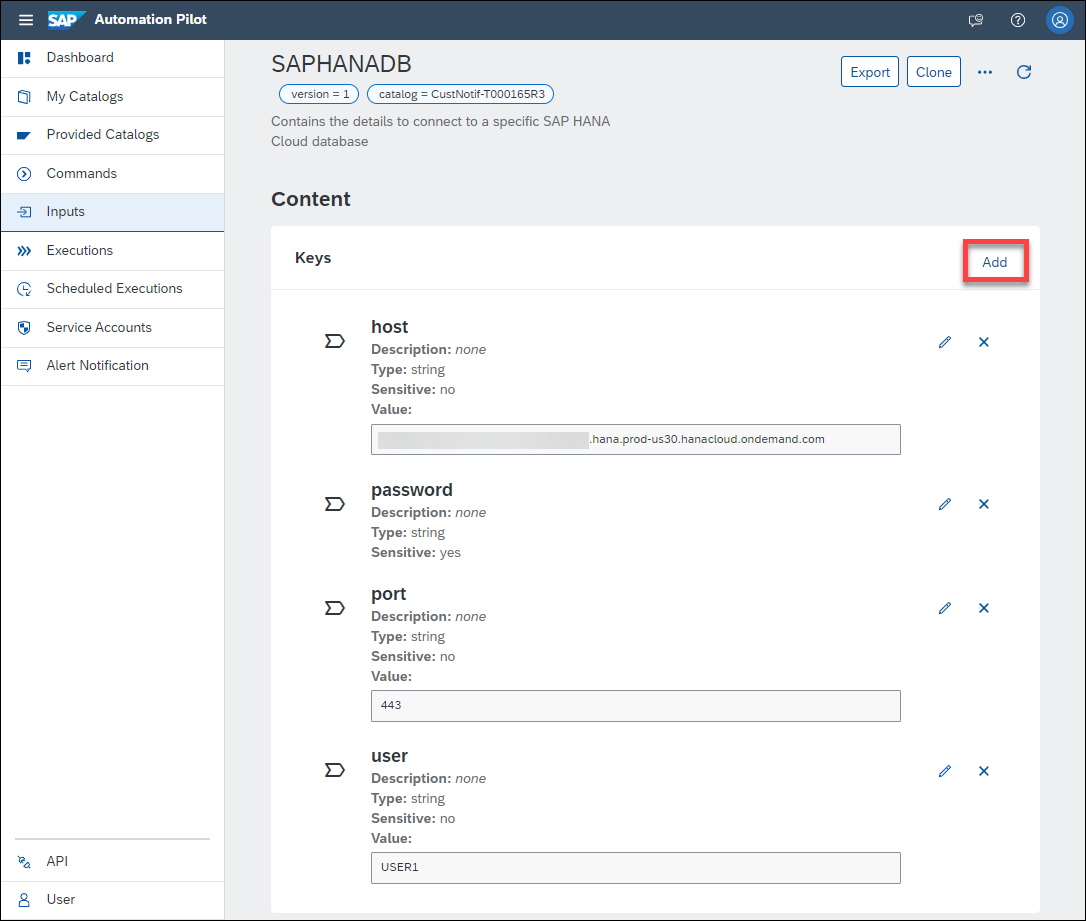
- Access to the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) that includes SAP HANA Cloud, SAP Alert Notification Service, and SAP Automation Pilot. These services are available in the SAP BTP free tier.
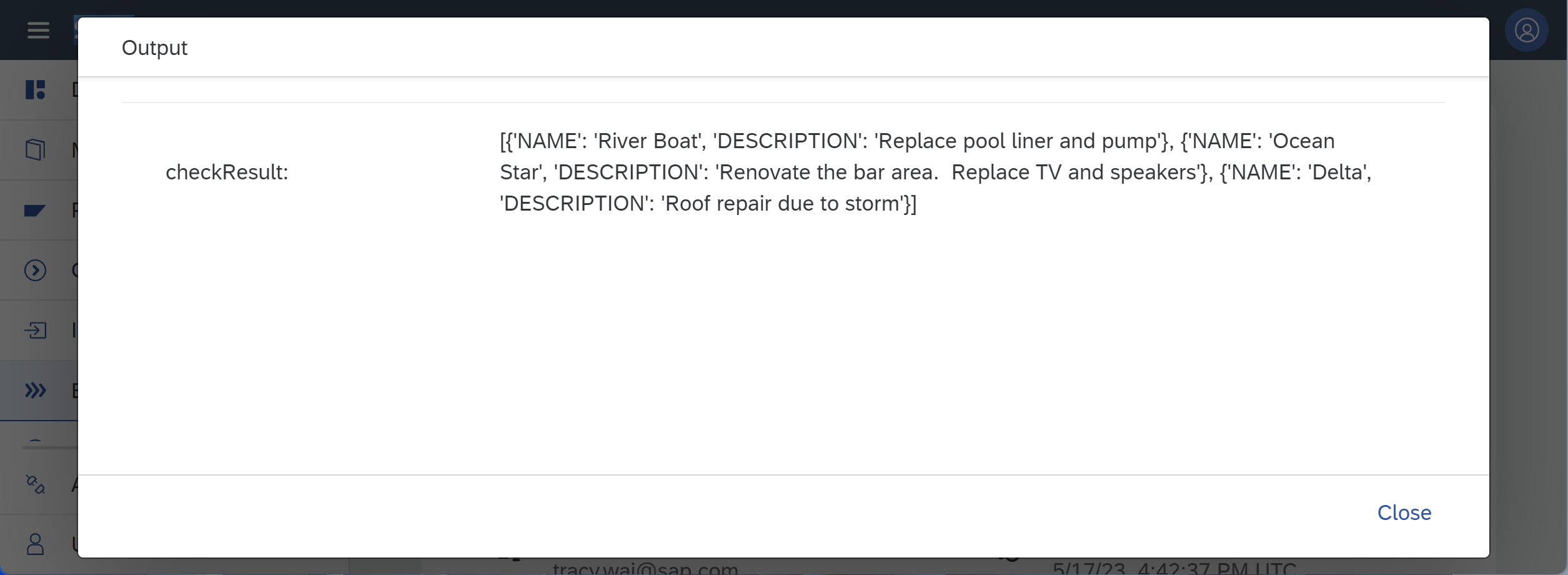
SAP HANA Cloud provides built-in alerts for items such as long running statements, table row counts, expiring database passwords, or low disk space. This tutorial will demonstrate an approach that can be used to create a notification for use cases not covered by the built-in alerts. The hotel dataset described in the tutorial Create Database Objects with SAP HANA Database Explorer contains a maintenance table where work items are described.
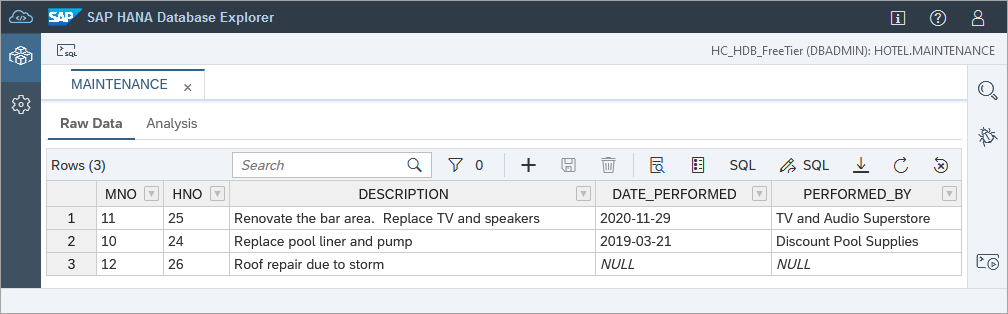
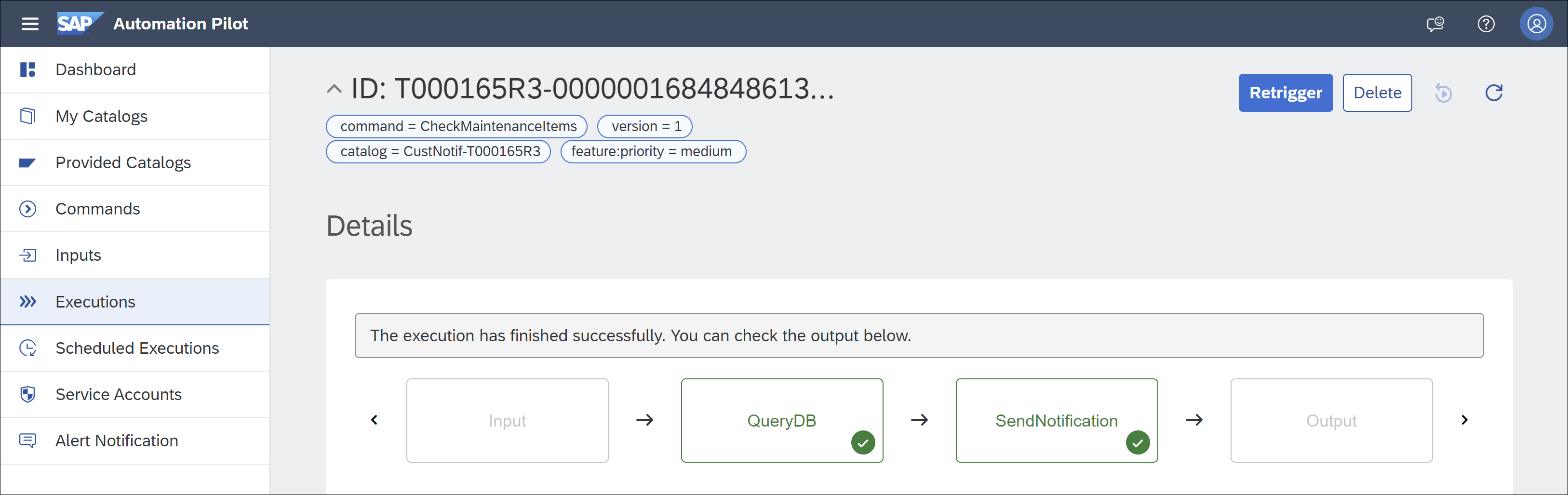
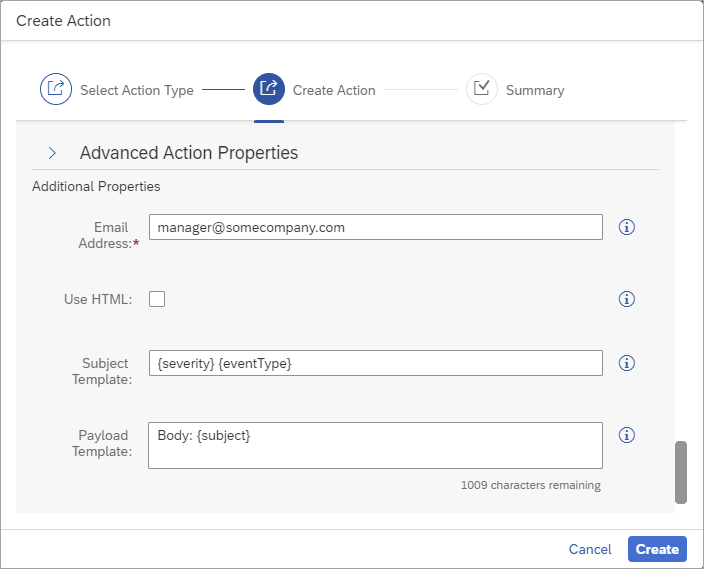
An SAP Automation Pilot command will be created to check if any maintenance items are unassigned, and if so, an email will be generated. The final step in the tutorial will demonstrate how to schedule the command to run once a week.

If you do not already have the
HOTEL.MAINTENANCEtable in an SAP HANA Cloud database, please create it now by following the first 2 steps in the Create Database Objects with SAP HANA Database Explorer tutorial.If you do not have a subscription to the SAP Automation Pilot service, step 1 of the tutorial Take Action Following a SAP HANA Cloud Database Alert with SAP Automation Pilot provides details on how to so.
If you do not have an instance of the SAP Alert Notification service, see step 5 of the tutorial Alerts in SAP HANA Database and Data Lake.