Model Data with SQL in SAP Datasphere
Get started with SQL views using the Data Builder in SAP Datasphere to create, visualize and manipulate data models.
You will learn
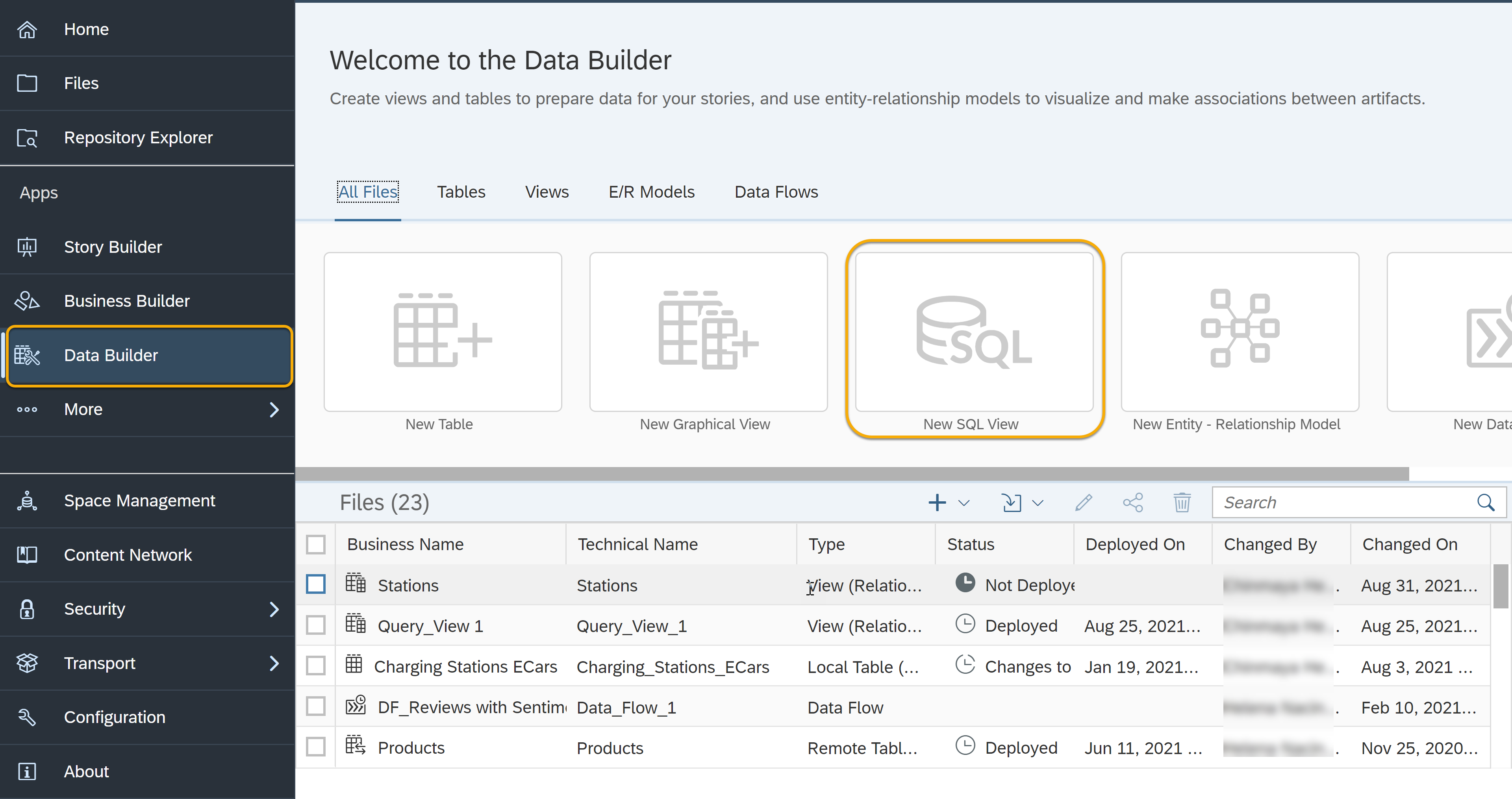
- How to create a SQL view in your Space
- How to preview and deploy a SQL view
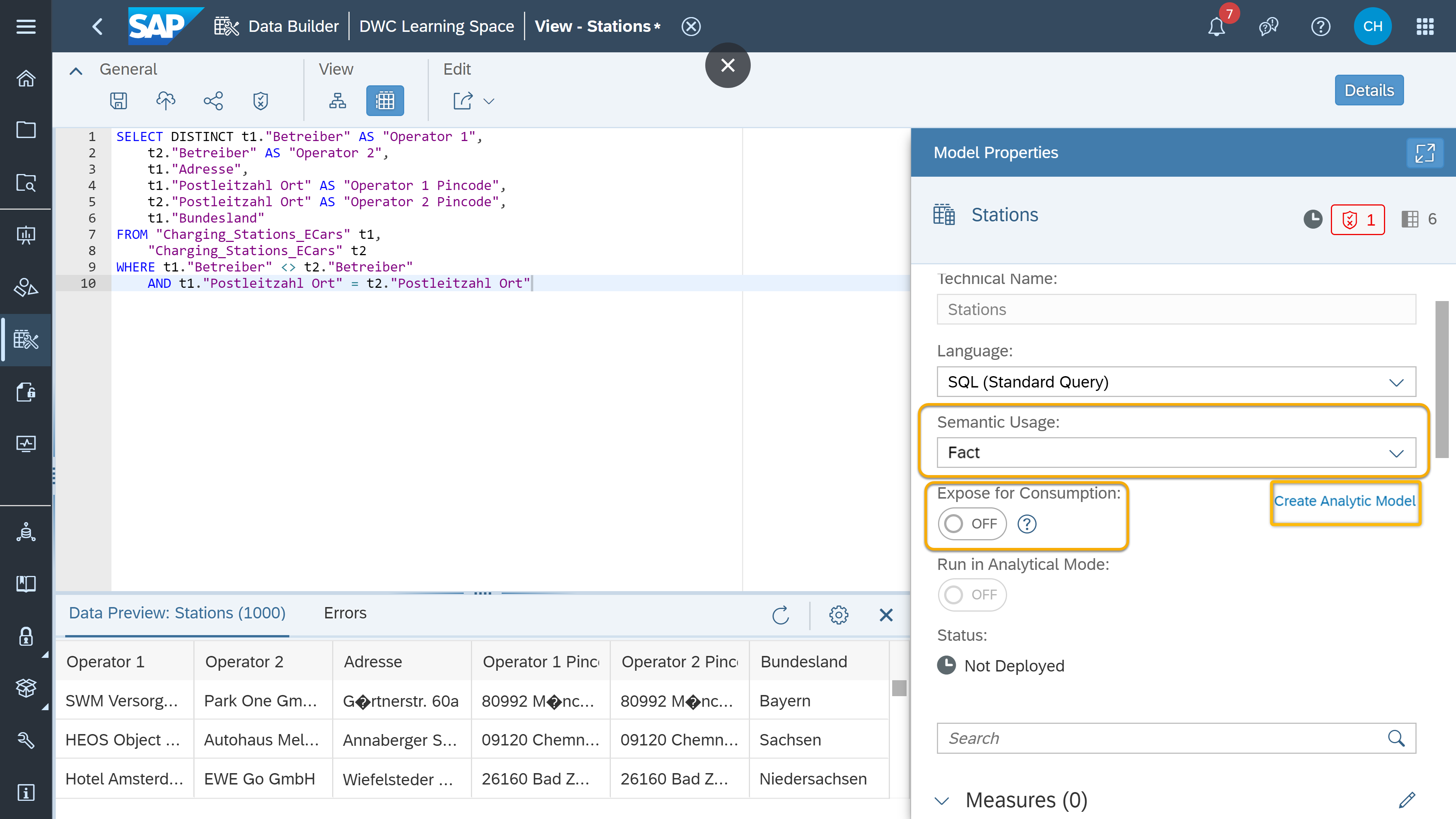
- How to use SAP HANA-based SQL script language in SAP Datasphere
Prerequisites
- You have your SAP Datasphere tenant or you have signed up for a SAP Datasphere free tier tenant.
- You have imported data into your Space.
SAP Datasphere is a flexible tool that allows you to model your data in whatever way you prefer: using graphical, drag-and-drop views, or using SQL statements. You can efficiently write SQL queries to manipulate data models and create SQL views in SAP Datasphere that will then feed business intelligence tools.
If you are unsure what data modeling means, or what a joins and unions are, please use our community blog posts to get familiar with these concepts:
• Data Modeling in SAP Datasphere
• Facts, Measures and Dimensions
Please note that SAP Data Warehouse Cloud has evolved into SAP Datasphere. While some screenshots in this tutorial reference SAP Data Warehouse Cloud, the content applies to SAP Datasphere.