Create an ABAP Database Table and Relevant ABAP Dictionary Objects
Beginner
1 hr. 15 min.
Create a database table from scratch using ABAP development tools for Eclipse (ADT); use different Data Dictionary objects to define the fields; then fill the table with test data.
You will learn
- How to create a table in ABAP, representing a table in your database
- How to create a reusable domain, which provides technical attributes for data elements
- How to create an elementary data type, or data element
- How to fill the table with three rows of test data
Prerequisites
- You have a valid instance of one of the following:
- SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) ABAP Environment. For more information, see Tutorial: Create Your First ABAP Console Application, steps 1-2.
- On-premise, .e.g. ABAP Cloud Developer Trial, 2022
- Tutorial: Create an ABAP Project in ABAP Development Tools (ADT)
- On this instance, you have pulled the SAP ABAP Flight Reference Scenario. To pull this reference scenario from
Github, see:
Downloading the ABAP Flight Reference Scenario
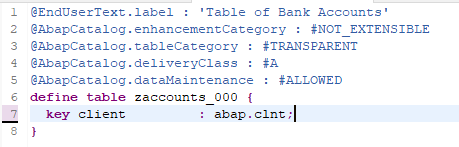
Tables are defined independently of the database in the ABAP Dictionary. When you activate the table in the Data Dictionary, the table is created in the underlying database.
The table in this tutorial will store bank account details for customers. The table will have the following columns (or fields):
client(key field)account_number(key field)bank_name(key field)bank_customer_idcitybalancecurrencyaccount_categorylastchangedat
Throughout this tutorial, replace
###or000with your initials or group number.