Access Remote Sources with SAP HANA Database Explorer
- How to use SAP HANA smart data access (SDA) to create connections (remote sources) to other databases
- How to create virtual tables from a remote source
- How to setup the Cloud Connector to enable a remote source from SAP HANA Cloud to an on-premise SAP HANA database
- Instances of SAP HANA, express edition, SAP HANA Cloud, SAP HANA database, and data lake Relational Engine
Prerequisites
- You have completed the first 3 tutorials in this group
- Two SAP HANA databases and an SAP HANA Cloud, data lake instance
Remote sources are connections to other databases. Virtual tables use a remote source to create a local table that points to data stored in another database. Federated queries make use of virtual and non virtual tables.
To illustrate these concepts, a table will be created in the remote database that contains fictitious review data from some of the top tourist sites near a given hotel. There is likely a correlation between hotel stays and the desire for customers to visit nearby tourist attractions or restaurants.
For additional details on SAP HANA smart data access (SDA) and SAP HANA Smart Data Integration (SDI), consult Connecting SAP HANA Cloud to Remote Data Sources and Data Access with SAP HANA Cloud.
This tutorial requires more than one database to complete. It is not necessary to complete this tutorial to continue to the next tutorial in this group.
The SAP HANA Cloud free tier or trial is limited to creating one SAP HANA database and one data lake instance.
The example in step 1 demonstrates connectivity from an on-premise, SAP HANA, express edition database to an SAP HANA Cloud database. The example in step 2 demonstrates a connection from an SAP HANA Cloud database to an SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Relational Engine. The example in step 3 demonstrates connecting from SAP HANA Cloud, database via the Cloud Connector to an SAP HANA, express edition database.
- Step 1
-
From the SAP HANA Cloud Central, open the SAP HANA database explorer and execute the following SQL statements to create the
tourist_reviewstable.If needed, first create a schema and user.
SQLCopyCREATE SCHEMA HOTELS; CREATE USER USER1 PASSWORD Password1 no force_first_password_change; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON SCHEMA HOTELS TO USER1;SQLCopySET SCHEMA HOTELS; CREATE COLUMN TABLE TOURIST_REVIEWS( review_id INTEGER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY, review_date DATE NOT NULL, destination_id INTEGER, destination_rating INTEGER, review VARCHAR(500) NOT NULL ); INSERT INTO TOURIST_REVIEWS(review_date, destination_id, destination_rating, review) VALUES('2019-03-15', 1, 5, 'We had a great day swimming at the beach and exploring the beach front shops. We will for sure be back next summer.'); INSERT INTO TOURIST_REVIEWS(review_date, destination_id, destination_rating, review) VALUES('2019-02-02', 1, 4, 'We had an enjoyable meal. The service and food was outstanding. Would have liked to have slightly larger portions'); -
The result can be seen below.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM TOURIST_REVIEWS;
-
To create a remote source from SAP HANA, express edition to SAP HANA Cloud, open the SAP HANA database explorer from the SAP HANA, express edition.
This step is optional for SAP HANA Cloud Trial users if you do not have an SAP HANA, express edition database. If you do not have an SAP HANA, express edition database, proceed to the next step which is Connect from SAP HANA Cloud to SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Relational Engine.
In a SQL console, enter the SQL statement below after adjusting the
ServerNode.SQLCopyCREATE REMOTE SOURCE REMOTE_HC ADAPTER "hanaodbc" CONFIGURATION 'ServerNode=XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX.hana.prod-ca10.hanacloud.ondemand.com:443;driver=libodbcHDB.so;dml_mode=readwrite;sslTrustStore="-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----MIIDrzCCApegAwIBAgIQCDvgVpBCRrGhdWrJWZHHSjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADBhMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEVMBMGA1UEChMMRGlnaUNlcnQgSW5jMRkwFwYDVQQLExB3d3cuZGlnaWNlcnQuY29tMSAwHgYDVQQDExdEaWdpQ2VydCBHbG9iYWwgUm9vdCBDQTAeFw0wNjExMTAwMDAwMDBaFw0zMTExMTAwMDAwMDBaMGExCzAJBgNVBAYTAlVTMRUwEwYDVQQKEwxEaWdpQ2VydCBJbmMxGTAXBgNVBAsTEHd3dy5kaWdpY2VydC5jb20xIDAeBgNVBAMTF0RpZ2lDZXJ0IEdsb2JhbCBSb290IENBMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA4jvhEXLeqKTTo1eqUKKPC3eQyaKl7hLOllsBCSDMAZOnTjC3U/dDxGkAV53ijSLdhwZAAIEJzs4bg7/fzTtxRuLWZscFs3YnFo97nh6Vfe63SKMI2tavegw5BmV/Sl0fvBf4q77uKNd0f3p4mVmFaG5cIzJLv07A6Fpt43C/dxC//AH2hdmoRBBYMql1GNXRor5H4idq9Joz+EkIYIvUX7Q6hL+hqkpMfT7PT19sdl6gSzeRntwi5m3OFBqOasv+zbMUZBfHWymeMr/y7vrTC0LUq7dBMtoM1O/4gdW7jVg/tRvoSSiicNoxBN33shbyTApOB6jtSj1etX+jkMOvJwIDAQABo2MwYTAOBgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMCAYYwDwYDVR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUA95QNVbRTLtm8KPiGxvDl7I90VUwHwYDVR0jBBgwFoAUA95QNVbRTLtm8KPiGxvDl7I90VUwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEFBQADggEBAMucN6pIExIK+t1EnE9SsPTfrgT1eXkIoyQY/EsrhMAtudXH/vTBH1jLuG2cenTnmCmrEbXjcKChzUyImZOMkXDiqw8cvpOp/2PV5Adg06O/nVsJ8dWO41P0jmP6P6fbtGbfYmbW0W5BjfIttep3Sp+dWOIrWcBAI+0tKIJFPnlUkiaY4IBIqDfv8NZ5YBberOgOzW6sRBc4L0na4UU+Krk2U886UAb3LujEV0lsYSEY1QSteDwsOoBrp+uvFRTp2InBuThs4pFsiv9kuXclVzDAGySj4dzp30d8tbQkCAUw7C29C79Fv1C5qfPrmAESrciIxpg0X40KPMbp1ZWVbd4=-----END CERTIFICATE-----"' WITH CREDENTIAL TYPE 'PASSWORD' USING 'user=User1;password=Password1'; CALL PUBLIC.CHECK_REMOTE_SOURCE('REMOTE_HC');Alternatively, you can create a remote source manually by right-clicking Remote Sources and select Add Remote Source.

Add a source name and specify the server, port, and credentials (USER1, Password1). The Extra Adapter properties can be retreived by copying the
sslTrustStorein the SQL query above.
Additional details can be found at CREATE REMOTE SOURCE Statement.
The ServerNode can be copied from SAP HANA Cloud Central by choosing Actions > Copy SQL Endpoint.

If the above command fails, one reason might be that an allowlist has been set on the SAP HANA Cloud instance. This can be seen by choosing Actions > Edit.

The public root certificate of the certificate authority (CA) that signed the SAP HANA Cloud instance’s server certificate is required in the
sslTrustStoreparameter. For more information, see Secure Communication Between SAP HANA Cloud and JDBC/ODBC Clients. -
After executing the create remote source SQL statement, the result can be seen in the Remote Sources folder, as shown below. You may need to press the refresh button.

-
A virtual table named
vt_tourist_reviewswill be created in SAP HANA, express edition. This will enable access to thetourist_reviewstable that was created in SAP HANA Cloud. This can be visualized as follows:
Open the SAP HANA database explorer from the SAP HANA, express edition.
If needed, create the HOTELS schema and a user who can access the schema.
SQLCopyCREATE USER USER1 PASSWORD Password1 no force_first_password_change; CREATE SCHEMA HOTELS; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON SCHEMA HOTELS TO USER1; -
Right-click the remote source named
REMOTE_HCand choose Open. -
Set the Schema to be
HOTELSand press the Search button.Check the
TOURIST_REVIEWScheckbox and press the Create Virtual Object(s) button.
-
Set the Object Name to be
VT_TOURIST_REVIEWSand the Schema to beHOTELS.Press the Create button.

Alternatively, the virtual table can also be created with the SQL statement below.
SQLCopyCREATE VIRTUAL TABLE VT_TOURIST_REVIEWS AT "REMOTE_HC"."HC_HDB".HOTELS."TOURIST_REVIEWS";Additional details can be found at CREATE VIRTUAL TABLE Statement.
-
Open the virtual table
VT_TOURIST_REVIEWSand notice that its type is virtual.
-
Perform queries against the local tables, the remote table, and perform a federated query that contains both local and remote tables.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM HOTELS.RESERVATION; SELECT * FROM HOTELS.CUSTOMER; SELECT * FROM HOTELS.VT_TOURIST_REVIEWS; SELECT C.NAME, TR.REVIEW, REVIEW_DATE FROM HOTELS.RESERVATION AS R JOIN HOTELS.VT_TOURIST_REVIEWS AS TR ON TR.REVIEW_DATE = R.ARRIVAL JOIN HOTELS.CUSTOMER AS C ON C.CNO = R.CNO;
Notice the executed time is greater when the data is retrieved from a virtual table.

-
Add a new review.
SQLCopyINSERT INTO HOTELS.VT_TOURIST_REVIEWS(review_id, review_date, destination_id, destination_rating, review) VALUES(3, '2020-08-21', 1, 5, 'The harbour cruise was fantastic. It was great to see the city from a different viewpoint'); SELECT * FROM HOTELS.VT_TOURIST_REVIEWS;Notice that the virtual table is editable.
A benefit of a virtual table is that there is no data movement. There is only one location where the data is persisted. As seen above, this can lead to longer query times when accessing remote data.
-
- Step 2
SAP HANA Cloud, data lake can be used to store large amounts of data that is not accessed and updated as frequently as data in an SAP HANA database. The following steps create the table
tourist_reviewsin SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Relational Engine and access the table from the associated SAP HANA database instance.-
If needed, in SAP HANA Cloud Central, add an SAP HANA Cloud, data lake instance to your SAP HANA Cloud instance, by choosing Actions > Add Data Lake.

-
Open the database explorer with a connection to the data lake by choosing Open in SAP HANA Database Explorer.
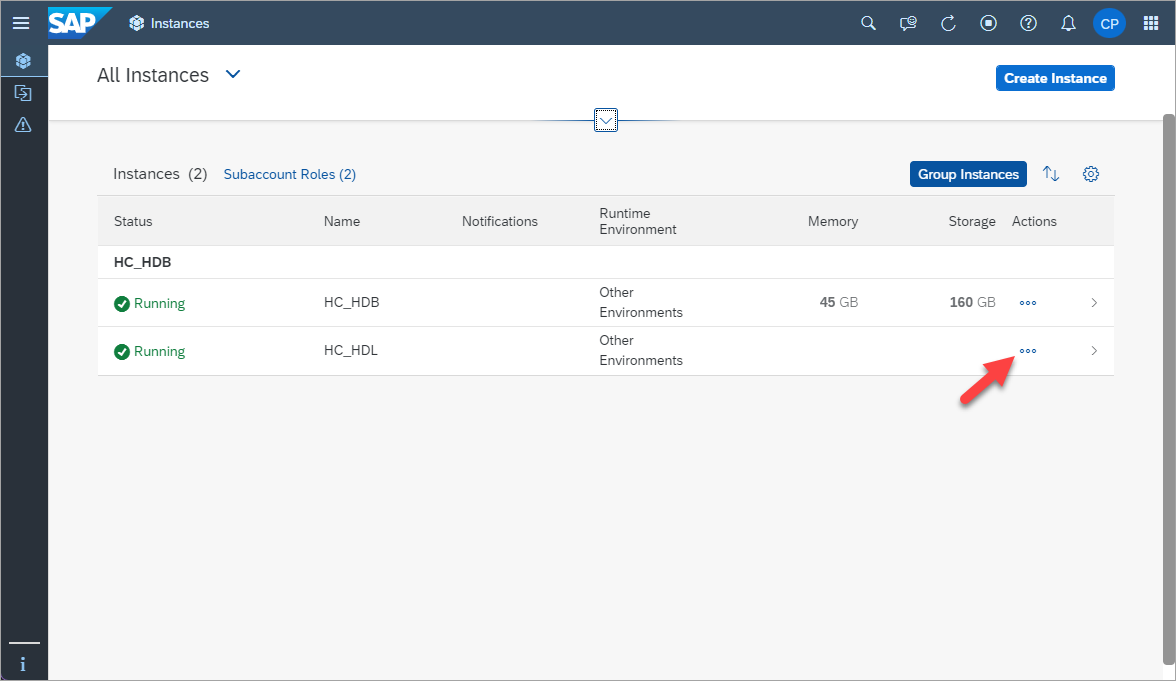
-
Execute the following SQL to create a table named
tourist_reviewsin the data lake Relational Engine.If needed, first create the required schema and role.
SQLCopy--Create a schema for the sample hotel dataset CREATE SCHEMA HOTELS; --Create USER1 and grant privileges CREATE USER USER1 IDENTIFIED BY Password1; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON SCHEMA HOTELS TO USER1; SET SCHEMA HOTELS; CREATE TABLE TOURIST_REVIEWS ( REVIEW_ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, REVIEW_DATE DATE NOT NULL, DESTINATION_ID INTEGER, DESTINATION_RATING INTEGER, REVIEW VARCHAR(500) NOT NULL ); INSERT INTO TOURIST_REVIEWS(REVIEW_ID, REVIEW_DATE, DESTINATION_ID, DESTINATION_RATING, REVIEW) VALUES(1, '2019-03-15', 1, 5, 'We had a great day swimming at the beach and exploring the beach front shops. We will for sure be back next summer.'); INSERT INTO TOURIST_REVIEWS(REVIEW_ID, REVIEW_DATE, DESTINATION_ID, DESTINATION_RATING, REVIEW) VALUES(2, '2019-02-02', 1, 4, 'We had an enjoyable meal. The service and food were outstanding. Would have liked to have slightly larger portions');
For additional details consult CREATE TABLE Statement for Data Lake Relational Engine.
-
In the SAP HANA database connection, create a remote source from the HANA database to the data lake Relational Engine. Be sure to replace the host and password values.
If you have not already done so, ensure that you have added USER1 to your SAP HANA data lake database, as shown in Step 1.
SQLCopyCREATE REMOTE SOURCE HC_DL ADAPTER "IQODBC" CONFIGURATION 'Driver=libdbodbc17_r.so;host=XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX.iq.hdl.trial-XXXX.hanacloud.ondemand.com:443;ENC=TLS(tls_type=rsa;direct=yes)' WITH CREDENTIAL TYPE 'PASSWORD' USING 'user=USER1;password=Password1'; CALL PUBLIC.CHECK_REMOTE_SOURCE('HC_DL');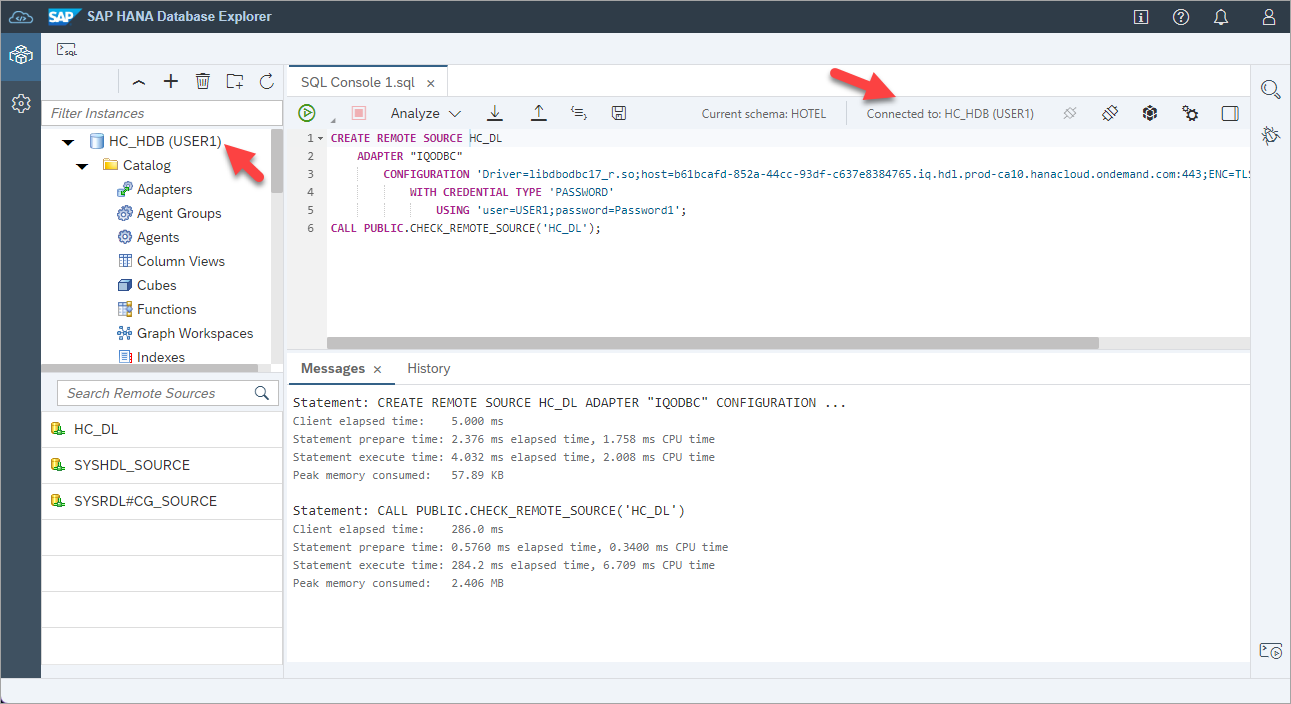
-
After pressing refresh, notice that under remote sources, there is a remote source
HC_DL.
-
Right-click on
HC_DLand choose Open. Create a virtual table in SAP HANA Cloud namedVT_DL_TOURIST_REVIEWSin the schema HOTELS that maps to the newly created table in SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Relational Engine.
This can be visualized as follows:

Alternatively, the following SQL statement can be used to create the virtual table.
SQLCopyCREATE VIRTUAL TABLE VT_DL_TOURIST_REVIEWS AT HC_DL.iqaas.HOTELS.TOURIST_REVIEWS;It is also possible to create the remote table and virtual table together in the same statement.
SQLCopyCREATE VIRTUAL TABLE VT_DL_TOURIST_REVIEWS ( REVIEW_ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, REVIEW_DATE DATE NOT NULL, DESTINATION_ID INTEGER, DESTINATION_RATING INTEGER, REVIEW VARCHAR(500) NOT NULL ) AT HC_DL.iqaas.HOTELS.TOURIST_REVIEWS WITH REMOTE; INSERT INTO VT_DL_TOURIST_REVIEWS VALUES(1, '2019-03-15', 1, 5, 'We had a great day swimming at the beach and exploring the beach front shops. We will for sure be back next summer.'); INSERT INTO VT_DL_TOURIST_REVIEWS VALUES(2, '2019-02-02', 1, 4, 'We had an enjoyable meal. The service and food were outstanding. Would have liked to have slightly larger portions'); -
Query the local SAP HANA table and the equivalent SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Relational Engine table.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM TOURIST_REVIEWS; SELECT * FROM VT_DL_TOURIST_REVIEWS;
-
Add a new review.
SQLCopyINSERT INTO VT_DL_TOURIST_REVIEWS VALUES(3, '2020-08-21', 1, 5, 'The harbour cruise was fantastic. It was great to see the city from a different viewpoint'); SELECT * FROM VT_DL_TOURIST_REVIEWS;Notice that the remote data source is updateable. Data stored in an SAP HANA Cloud, data lake is stored on disk, which has cost advantages compared to memory storage. SAP HANA Cloud, data lake can also be used to store large amounts of data.
Another approach is to use a relational container. For additional details see Manage Relational Containers in Data Lake Relational Engine (SAP HANA DB-Managed). An example follows.
SQLCopyCALL SYSHDL.CREATE_CONTAINER('HOTELS_CONTAINER', 'DBADMIN'); CREATE VIRTUAL TABLE TOURIST_REVIEWS ( REVIEW_ID INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, REVIEW_DATE DATE NOT NULL, DESTINATION_ID INTEGER, DESTINATION_RATING INTEGER, REVIEW VARCHAR(500) NOT NULL ) at "SYSHDL_HOTELS_CONTAINER_SOURCE"."<NULL>"."SYSHDL_HOTELS_CONTAINER"."TOURIST_REVIEWS" WITH REMOTE; INSERT INTO TOURIST_REVIEWS(REVIEW_ID, REVIEW_DATE, DESTINATION_ID, DESTINATION_RATING, REVIEW) VALUES(1, '2019-03-15', 1, 5, 'We had a great day swimming at the beach and exploring the beach front shops. We will for sure be back next summer.'); CALL SYSHDL_HOTELS_CONTAINER.REMOTE_EXECUTE('INSERT INTO TOURIST_REVIEWS VALUES(2, ''2019-02-02'', 1, 4, ''We had an enjoyable meal. The service and food was outstanding. Would have liked to have slightly larger portions'')'); --GRANT SYSHDL_HOTELS_CONTAINER_ROLE TO USER1; --CONNECT USER1 PASSWORD Password1; SELECT * FROM SYSHDL_HOTELS_CONTAINER.TOURIST_REVIEWS; CALL SYSHDL_HOTELS_CONTAINER.REMOTE_EXECUTE('DROP TABLE SYSHDL_HOTELS_CONTAINER.TOURIST_REVIEWS;'); --CONNECT DBADMIN PASSWORD Hana1234; CALL SYSHDL.DELETE_CONTAINER('HOTELS_CONTAINER');
-
- Step 3
The Cloud Connector enables communication from the SAP BTP running in the public internet to securely connect to a configured on-premise system such as SAP HANA, express edition.
-
Enable the Cloud Connector connectivity in SAP HANA Cloud Central: Actions > Manage Configuration > Edit.

-
Download the Cloud Connector. The software needs to run on a machine that can access your on-premise SAP HANA instance. In this example, the Cloud Connector is running on Windows and is accessing an SAP HANA, express edition database running in a VM on the same machine.
-
As described at Installation on Microsoft Windows OS, a Java JDK is required.
The following commands were used to start the Cloud Connector.
Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copyset PATH=<Java Installation Directory\bin>;C:\Windows\System32 set JAVA_HOME=<Java Installation Directory> cd C:\SAP\CC go.bat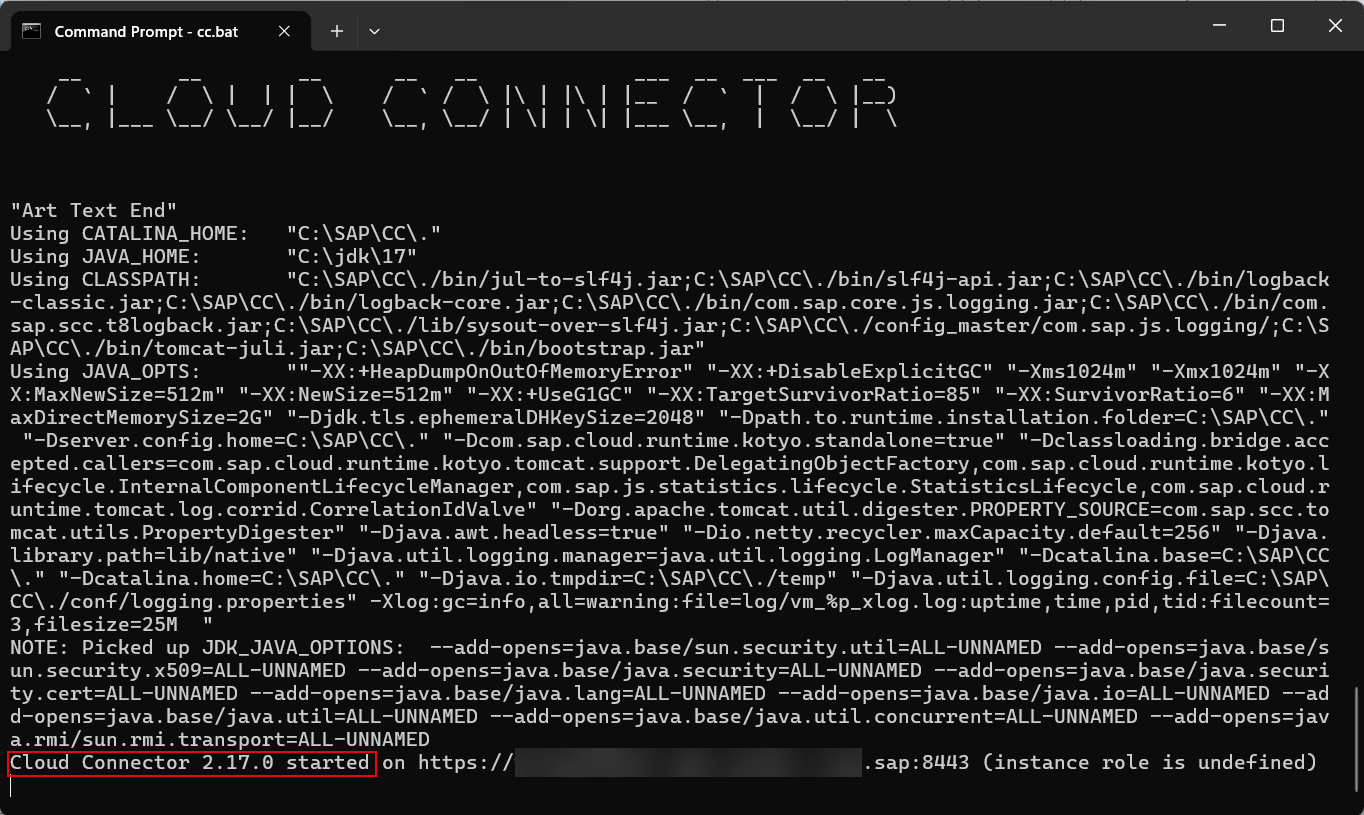
It may take a while to start the Cloud Connector and a line such as Cloud Connector 2.17.0 started will appear as shown above when it is started.
-
In a browser, open the URL https://localhost:8443.
The initial user name and password are Administrator and manage.
-
Configure the Cloud Connector to connect to the Cloud Foundry subaccount.

The location ID is used when multiple Cloud Connectors are connected to the same subaccount
If you are an SAP employee, you may need to enter your password + a time-based passcode as the password.
The region and subaccount ID can be found in the SAP BTP cockpit.
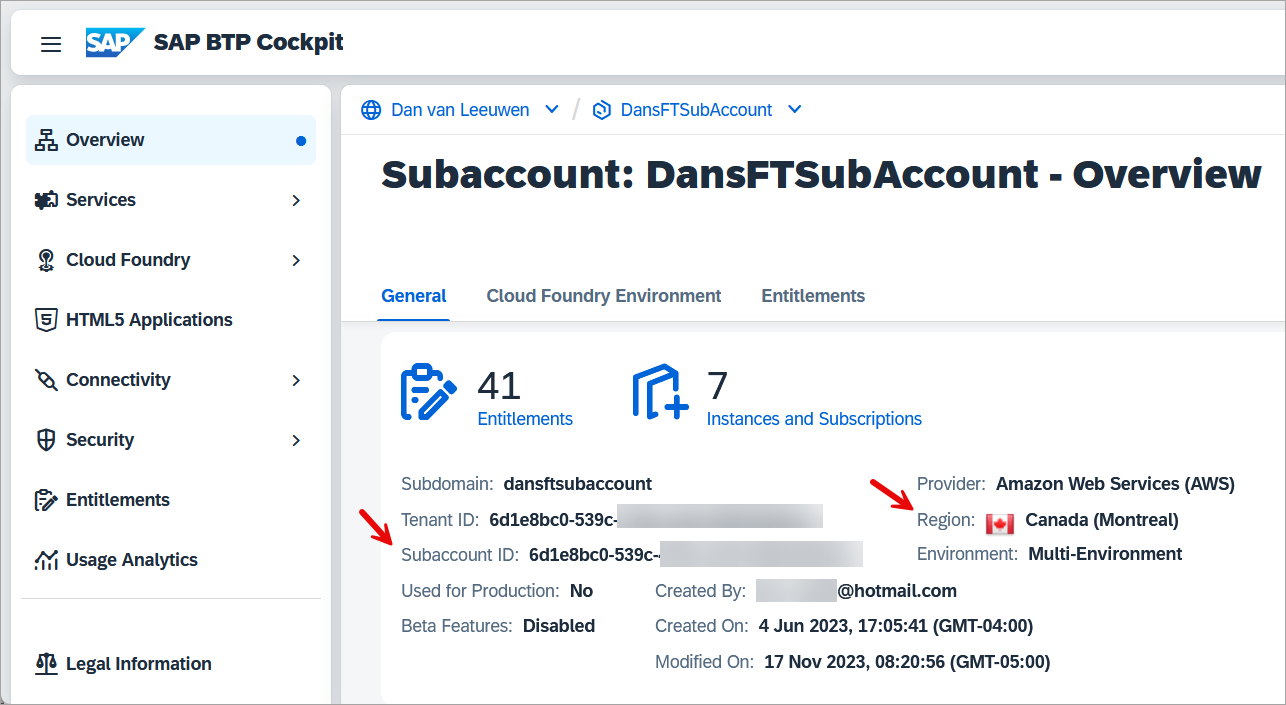
The screen below shows a successful connection.

For additional details, see Initial Configuration.
-
Configure the Cloud Connector to connect to the on-premise database.
Select Cloud To On-Premise and press the + icon.
Select SAP HANA for the back-end type.
Select TCP for the protocol.
Specify the host and port for the SAP HANA, express database.
The virtual name and port can be different.

Once the cloud connector has been installed and configured to connect to a BTP subaccount, it will appear as shown below in the SAP BTP Cockpit.

-
In the SAP HANA database explorer connected to SAP HANA Cloud, right-click Remote Sources and select Add Remote Source.

Specify the server, port, extra adapter properties, credentials (User1, Password1) and if a Location ID was specified in step 5, add
scc_location_id=<locationid>'to the Extra Adapter Properties.
Alternatively, in a SQL console, enter the SQL statement below after adjusting the
ServerNode.SQLCopyCREATE REMOTE SOURCE REMOTE_HANA_EXPRESS ADAPTER "hanaodbc" CONFIGURATION 'ServerNode=hxehost:39015;use_haas_socks_proxy=true;driver=libodbcHDB.so;' WITH CREDENTIAL TYPE 'PASSWORD' USING 'user=User1;password=Password1'; CALL PUBLIC.CHECK_REMOTE_SOURCE('REMOTE_HANA_EXPRESS');Additional details can be found at Create an SAP HANA On-Premise Remote Source.
-
After executing the create remote source SQL statement, the result can be seen in the Remote Sources folder, as shown below. You may need to press the refresh button.
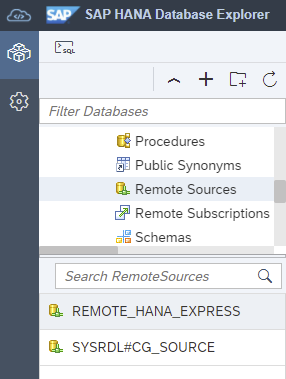
-
Right-click the remote source named
REMOTE_HANA_EXPRESSand choose Open. -
Set the Schema to be
HOTELSand press the Search button.
Notice that it is possible to create virtual tables to access the data from the on-premise system in SAP HANA Cloud.
This can be visualized as follows:

For further information, see Data Replication and Data Virtualization, Access Data Across Your On-Premise and Cloud Data Sources, and Getting Started with SAP HANA Cloud | Remote Data Source.
-
- Step 4
Congratulations! You have now used remote sources to access data running on a different SAP HANA instance and on an SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Relational Engine.
Which of the following are true for virtual tables?