Export and Import Data and Schema with SAP HANA Database Explorer
- How to export and import data using the export and import data wizards, SQL statements export into and import from, and the download option in the SQL console results tab
- How to export and import schema objects using export and import catalog wizards and the SQL statements export and import
- How to use cloud storage providers as a target when exporting or importing
Prerequisites
- An SAP HANA database such as SAP HANA Cloud trial, free tier, or the SAP HANA, express edition that includes the SAP HANA database explorer
- Data lake Files, Amazon AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure accounts will be needed for optional steps in this tutorial.
- You have completed the first 3 tutorials in this group.
The following steps will demonstrate a few ways to export and import data such as the contents of tables or views as well how to export and import database schema or catalog objects.
A few differences between exporting and importing data and importing and exporting catalog objects are:
- Data export and import works with one table or view
- Catalog export or import works with more than one object at one time
- Catalog export or import can include additional objects such as functions and procedures
- Catalog export or import includes the SQL to recreate the object
- Step 1
The following tables list the different options available in the SAP HANA database explorer to export and import data from a single table or view.
Methods to export tables or views
Method Version Target Format(s) Export from SQL console All local computer CSV Export data wizard SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database data lake Files, S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS CSV, Parquet, JSON (for document stores) Export into statement SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database data lake Files, S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS CSV, Parquet, JSON (for document stores) Export into statement SAP HANA on-premise SAP HANA file system CSV Methods to import into tables
Method Version Source Format(s) Notes Import data wizard All local computer CSV 1 GB max, 2 MB per row in SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database; 200 MB max SAP HANA on-premise Import data wizard SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database data lake Files, S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS CSV, Parquet, JSON (for document stores) Import data wizard SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database data lake Files, local computer, S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS ESRI shapefilesAn example of importing an ESRI shapefilecan be found in Try Out Multi-Model Functionality with the SAP HANA Database Explorer tutorial.Import data wizard SAP HANA on-premise SAP HANA file system CSV Target table can be created Import from statement SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database data lake Files, S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS CSV, Parquet, JSON (for document stores) Import from statement SAP HANA on-premise SAP HANA file system CSV Insert into table name select from statement All local or remote tables select statement The following steps will attempt to demonstrate an export and import of data from the maintenance table using the download option from the SQL console and the import data wizard.
-
Enter the SQL statement below.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM MAINTENANCE;Left-click on the download toolbar item.

Choose Download.

There is a setting that controls the number of results displayed which may need to be adjusted for tables with larger results.

-
Enter the SQL statement below to delete the rows in the table. They will be added back in the next sub-step.
SQLCopyDELETE FROM MAINTENANCE; -
Right-click on the maintenance table and choose Import Data.

Browse to the previously downloaded CSV file and complete the wizard.

The header row in the
data.csvfile is used to set the initial values of the source column to database column mappings.
Complete the wizard.

After completing the wizard, the contents of the maintenance table should now be the same as it was before the previously executed delete statement.
-
With SAP HANA, express edition, the following statements can be executed to export and import from a directory on the SAP HANA file system assuming that the directory exists and the user
hxeadmhas permission to access it.SQLCopyEXPORT INTO '/tmp/export/maintenance.csv' FROM MAINTENANCE WITH COLUMN LIST IN FIRST ROW; DELETE FROM MAINTENANCE; ALTER SYSTEM ALTER CONFIGURATION ('indexserver.ini', 'system') set ('import_export', 'csv_import_path_filter') = '/tmp/export' WITH RECONFIGURE; IMPORT FROM CSV FILE '/tmp/export/maintenance.csv' INTO MAINTENANCE WITH COLUMN LIST IN FIRST ROW ERROR LOG 'error_log.txt' FAIL ON INVALID DATA;
-
- Step 2
The following steps are for illustrative purposes only and are not meant to be followed. Complete steps for working with cloud storage services are provided in steps 3, 4, 6, and 7.
-
With SAP HANA Cloud, an export data wizard is available.

It can be used to export data to cloud storage providers such as SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Files, Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Storage, and Alibaba Cloud OSS.

The screenshot below shows the data lake Files being used as an export target.

Once the wizard has finished, the exported CSV file can be seen in the data lake Files container.

The wizard makes use of the export into statement. An example is shown below:
SQLCopyEXPORT INTO CSV FILE 'hdlfs://1234-567-890-1234-56789.files.hdl.prod-us10.hanacloud.ondemand.com/HOTELS/maintenance.csv' FROM MAINTENANCE WITH CREDENTIAL 'DL_FILES' COLUMN LIST IN FIRST ROW; -
The import data wizard provides a corresponding option to import from cloud storage providers.

The wizard makes use of the import from statement. An example is shown below:
SQLCopy--DELETE FROM MAINTENANCE; IMPORT FROM PARQUET FILE 'azure://danstestsa:sp=racwdl&st=2021-01-09T13:00:46Z&se=2021-01-10T13:00:46Z&sv=2019-12-12&sr=c&sig=TP%2BVYhcvSPDc4DZxcls6vN%2BCLHDNagedbei2IuEZsWU%3D@myblobcontainer/maintenance.parquet' INTO MAINTENANCE WITH FAIL ON INVALID DATA;
-
- Step 3
The following steps walk through the process of exporting to and importing data using data lake Files with a SAP HANA Cloud, SAP HANA database. This step requires a productive SAP HANA Cloud data lake instance as data lake files is currently not part of free tier or trial.
-
Complete steps 3 and 4 in the Getting Started with Data Lake Files HDLFSCLI tutorial to configure the trust setup of the data lake Files container.
-
Add the data lake Files container to the SAP HANA database explorer.

The REST API endpoint can be copied from the instances action menu in SAP HANA Cloud Central.

After the data lake Files container has been added, files can be uploaded, viewed, or deleted.

-
Create a database credential for the data lake Files container. Further details are described at Importing and Exporting with SAP HANA Cloud Data Lake Files Storage.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM PSES; CREATE PSE HTTPS; SELECT SUBJECT_COMMON_NAME, CERTIFICATE_ID, COMMENT, CERTIFICATE FROM CERTIFICATES; --cert from https://dl.cacerts.digicert.com/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem and is the CA for HANA Cloud CREATE CERTIFICATE FROM '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----MIIDrzCCApegAwIBAgIQCDvgVpBCRrGhdWrJWZHHSjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADBh MQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEVMBMGA1UEChMMRGlnaUNlcnQgSW5jMRkwFwYDVQQLExB3 d3cuZGlnaWNlcnQuY29tMSAwHgYDVQQDExdEaWdpQ2VydCBHbG9iYWwgUm9vdCBD QTAeFw0wNjExMTAwMDAwMDBaFw0zMTExMTAwMDAwMDBaMGExCzAJBgNVBAYTAlVT MRUwEwYDVQQKEwxEaWdpQ2VydCBJbmMxGTAXBgNVBAsTEHd3dy5kaWdpY2VydC5j b20xIDAeBgNVBAMTF0RpZ2lDZXJ0IEdsb2JhbCBSb290IENBMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG 9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA4jvhEXLeqKTTo1eqUKKPC3eQyaKl7hLOllsB CSDMAZOnTjC3U/dDxGkAV53ijSLdhwZAAIEJzs4bg7/fzTtxRuLWZscFs3YnFo97 nh6Vfe63SKMI2tavegw5BmV/Sl0fvBf4q77uKNd0f3p4mVmFaG5cIzJLv07A6Fpt 43C/dxC//AH2hdmoRBBYMql1GNXRor5H4idq9Joz+EkIYIvUX7Q6hL+hqkpMfT7P T19sdl6gSzeRntwi5m3OFBqOasv+zbMUZBfHWymeMr/y7vrTC0LUq7dBMtoM1O/4 gdW7jVg/tRvoSSiicNoxBN33shbyTApOB6jtSj1etX+jkMOvJwIDAQABo2MwYTAO BgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMCAYYwDwYDVR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUA95QNVbR TLtm8KPiGxvDl7I90VUwHwYDVR0jBBgwFoAUA95QNVbRTLtm8KPiGxvDl7I90VUw DQYJKoZIhvcNAQEFBQADggEBAMucN6pIExIK+t1EnE9SsPTfrgT1eXkIoyQY/Esr hMAtudXH/vTBH1jLuG2cenTnmCmrEbXjcKChzUyImZOMkXDiqw8cvpOp/2PV5Adg 06O/nVsJ8dWO41P0jmP6P6fbtGbfYmbW0W5BjfIttep3Sp+dWOIrWcBAI+0tKIJF PnlUkiaY4IBIqDfv8NZ5YBberOgOzW6sRBc4L0na4UU+Krk2U886UAb3LujEV0ls YSEY1QSteDwsOoBrp+uvFRTp2InBuThs4pFsiv9kuXclVzDAGySj4dzp30d8tbQk CAUw7C29C79Fv1C5qfPrmAESrciIxpg0X40KPMbp1ZWVbd4=-----END CERTIFICATE-----' COMMENT 'SAP_HC'; --DROP CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>;Now you can add the certificate to the PSE. Execute the following to retrieve the certificate ID.
SQLCopySELECT CERTIFICATE_ID FROM CERTIFICATES WHERE COMMENT = 'SAP_HC'; --CERTIFICATE_IDAdd the certificate ID (ex: 123456) from the previous statement into
<CERTIFICATE_ID>.SQLCopyALTER PSE HTTPS ADD CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>; --ALTER PSE HTTPS DROP CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>;Then, set the own certificate with the client private key, client certificate, and Root Certification Authority of the client certificate in plain text. Make sure you have completed steps 3 and 4 in the Getting Started with Data Lake Files HDLFSCLI tutorial to configure the trust setup of the data lake Files container.
SQLCopyALTER PSE HTTPS SET OWN CERTIFICATE '<Contents from client.key> <Contents from client.crt> <Contents from ca.crt>'; --GRANT REFERENCES ON PSE HTTPS TO USER1; SELECT * FROM PSE_CERTIFICATES;The above commands create a personal security environment (PSE), create a certificate, and add the certificate to the PSE.
-
Execute the following SQL to store a credential in the database for the user.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM CREDENTIALS; CREATE CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHANAIMPORTEXPORT' PURPOSE 'DL_FILES' TYPE 'X509' PSE HTTPS;You can now use the Database Credential to import/export data.
-
Export the table
MAINTENANCEinto the data lake Files container.
The wizard makes use of the export from statement. An example is shown below:
SQLCopyEXPORT INTO CSV FILE 'hdlfs://1234-567-890-1234-56789.files.hdl.prod-us10.hanacloud.ondemand.com/HOTELS/maintenance.csv' FROM MAINTENANCE WITH CREDENTIAL 'DL_FILES' COLUMN LIST IN FIRST ROW; -
Enter the SQL statement below to delete the rows in the table. They will be added back in the next sub-step when the import command is shown.
SQLCopyDELETE FROM MAINTENANCE; -
Right-click on the maintenance table and choose Import Data.

From the Import data from drop down, select Data Lake Files.

The wizard makes use of the import from statement. An example is shown below.
SQLCopyIMPORT FROM CSV FILE 'hdlfs://1234-567-890-1234-56789.files.hdl.prod-us10.hanacloud.ondemand.com/HOTELS/maintenance.csv' INTO MAINTENANCE WITH CREDENTIAL 'DL_FILES' COLUMN LIST IN FIRST ROW FAIL ON INVALID DATA;
-
- Step 4
The following steps walk through the process of exporting to and importing data using data lake Files with a SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Relational Engine database. This step requires a productive SAP HANA Cloud data lake instance as data lake files is currently not part of free tier or trial. The following steps assume you have followed the first two sub steps in the previous step so that a data lake Files connection has been added to the SAP HANA database explorer.
-
Create a database credential for the data lake Files container. This step is required if you wish to export to a data lake Files instance that is not the one associated with the data lake Relational Engine. Further details are described at Unloading Data to Data Lake Files from Data Lake Relational Engine. Open a SQL Console connected to a data lake Relational Engine instance and execute the below SQL statements.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM SYSPSE; CREATE PSE HTTPS; SELECT * FROM SYSCERTIFICATE WHERE cert_name = 'DigiCertRootCA'; ALTER PSE HTTPS ADD CERTIFICATE <object_id>;SQLCopySELECT * FROM SYSPSECERTIFICATE; ALTER PSE HTTPS SET OWN CERTIFICATE '<Contents from client.key> <Contents from client.crt> <Contents from ca.crt>'; ----ALTER PSE HTTPS UNSET OWN CERTIFICATE;SQLCopySELECT * FROM SYSCREDENTIAL; CREATE CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHDLRELOADUNLOAD' PURPOSE 'DL_FILES' TYPE 'X509' PSE HTTPS; --DROP CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHDLRELOADUNLOAD' PURPOSE 'DL_FILES' TYPE 'X509'; -
Export or unload the data from the MAINTENANCE table to a data lake Files instance. Note that the CONNECTION_STRING and WITH CREDENTIALS are not required if you are targeting the associated data lake Files instance.
SQLCopyUNLOAD SELECT * FROM HOTELS.MAINTENANCE INTO FILE 'hdlfs:///maint.csv' NULL FORMAT EMPTY CONNECTION_STRING 'ENDPOINT=060acb0b-de9b-4801-9aa0-0dcfe503f0f0.files.hdl.prod-us10.hanacloud.ondemand.com' WITH CREDENTIAL 'DL_FILES'; -
Import or load the data back into the MAINTENANCE table.
SQLCopyDELETE FROM HOTELS.MAINTENANCE; LOAD TABLE HOTELS.MAINTENANCE (MNO, HNO, DESCRIPTION, DATE_PERFORMED, PERFORMED_BY) FROM 'hdlfs:///maint.csv' CONNECTION_STRING 'ENDPOINT=https://060acb0b-de9b-4801-9aa0-0dcfe503f0f0.files.hdl.prod-us10.hanacloud.ondemand.com' WITH CREDENTIAL 'DL_FILES' ESCAPES OFF;
Additional details can be found at Unloading Data to Data Lake Files from Data Lake Relational Engine and Loading Data From Data Lake Files to Data Lake Relational Engine.
-
- Step 5
The following steps walk through the process of exporting to and importing data from Google Cloud Storage service with a SAP HANA Cloud, SAP HANA database.
-
Sign in to the Google Cloud Console.
-
Create a project.

-
Navigate to Cloud Storage.

-
Create a bucket.

-
Navigate to IAM & Admin.
-
Create a service account.

Add the Owner role so that the service account can access the resources in the project.

-
In the generated service account, add a key.

Once complete, a JSON file will be downloaded that contains the
client_emailandprivate_keywhich will be used when accessing the bucket. -
Remove any line breaks (i.e. \n) from the private key. This can be done by pasting the private key into a new SQL console and opening the search and replace menu (Ctrl-F).

-
Create Credentials (Recommended)
You can view your service account email in the Service Accounts tab.

Execute the following SQL to store the private key and service account as a credential in the database. Paste the service account email and private key as user and password.
SQLCopyCREATE CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHANAIMPORTEXPORT' PURPOSE 'GoogleCloud' TYPE 'PASSWORD' USING 'user=<client_email>;password=<private_key>'; SELECT * FROM CREDENTIALS; --DROP CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHANAIMPORTEXPORT' PURPOSE 'GoogleCloud' TYPE 'PASSWORD';
Additional details can be found at CREATE CREDENTIAL Statement and CREDENTIALS System View.
-
A Google Storage SSL certificate is required to connect to the Google Cloud Storage bucket via the SAP HANA Cloud, SAP HANA database. Open your SQL console within SAP HANA database explorer and run the following commands to create a certificate.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM PSES; CREATE PSE HTTPS; SELECT SUBJECT_COMMON_NAME, CERTIFICATE_ID, COMMENT, CERTIFICATE FROM CERTIFICATES; CREATE CERTIFICATE FROM '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIFVzCCAz+gAwIBAgINAgPlk28xsBNJiGuiFzANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQwFADBHMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzEiMCAGA1UEChMZR29vZ2xlIFRydXN0IFNlcnZpY2VzIExMQzEU MBIGA1UEAxMLR1RTIFJvb3QgUjEwHhcNMTYwNjIyMDAwMDAwWhcNMzYwNjIyMDAw MDAwWjBHMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEiMCAGA1UEChMZR29vZ2xlIFRydXN0IFNlcnZp Y2VzIExMQzEUMBIGA1UEAxMLR1RTIFJvb3QgUjEwggIiMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUA A4ICDwAwggIKAoICAQC2EQKLHuOhd5s73L+UPreVp0A8of2C+X0yBoJx9vaMf/vo 27xqLpeXo4xL+Sv2sfnOhB2x+cWX3u+58qPpvBKJXqeqUqv4IyfLpLGcY9vXmX7w Cl7raKb0xlpHDU0QM+NOsROjyBhsS+z8CZDfnWQpJSMHobTSPS5g4M/SCYe7zUjw TcLCeoiKu7rPWRnWr4+wB7CeMfGCwcDfLqZtbBkOtdh+JhpFAz2weaSUKK0Pfybl qAj+lug8aJRT7oM6iCsVlgmy4HqMLnXWnOunVmSPlk9orj2XwoSPwLxAwAtcvfaH szVsrBhQf4TgTM2S0yDpM7xSma8ytSmzJSq0SPly4cpk9+aCEI3oncKKiPo4Zor8 Y/kB+Xj9e1x3+naH+uzfsQ55lVe0vSbv1gHR6xYKu44LtcXFilWr06zqkUspzBmk MiVOKvFlRNACzqrOSbTqn3yDsEB750Orp2yjj32JgfpMpf/VjsPOS+C12LOORc92 wO1AK/1TD7Cn1TsNsYqiA94xrcx36m97PtbfkSIS5r762DL8EGMUUXLeXdYWk70p aDPvOmbsB4om3xPXV2V4J95eSRQAogB/mqghtqmxlbCluQ0WEdrHbEg8QOB+DVrN VjzRlwW5y0vtOUucxD/SVRNuJLDWcfr0wbrM7Rv1/oFB2ACYPTrIrnqYNxgFlQID AQABo0IwQDAOBgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMCAYYwDwYDVR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zAdBgNVHQ4E FgQU5K8rJnEaK0gnhS9SZizv8IkTcT4wDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEMBQADggIBAJ+qQibb C5u+/x6Wki4+omVKapi6Ist9wTrYggoGxval3sBOh2Z5ofmmWJyq+bXmYOfg6LEe QkEzCzc9zolwFcq1JKjPa7XSQCGYzyI0zzvFIoTgxQ6KfF2I5DUkzps+GlQebtuy h6f88/qBVRRiClmpIgUxPoLW7ttXNLwzldMXG+gnoot7TiYaelpkttGsN/H9oPM4 7HLwEXWdyzRSjeZ2axfG34arJ45JK3VmgRAhpuo+9K4l/3wV3s6MJT/KYnAK9y8J ZgfIPxz88NtFMN9iiMG1D53Dn0reWVlHxYciNuaCp+0KueIHoI17eko8cdLiA6Ef MgfdG+RCzgwARWGAtQsgWSl4vflVy2PFPEz0tv/bal8xa5meLMFrUKTX5hgUvYU/ Z6tGn6D/Qqc6f1zLXbBwHSs09dR2CQzreExZBfMzQsNhFRAbd03OIozUhfJFfbdT 6u9AWpQKXCBfTkBdYiJ23//OYb2MI3jSNwLgjt7RETeJ9r/tSQdirpLsQBqvFAnZ 0E6yove+7u7Y/9waLd64NnHi/Hm3lCXRSHNboTXns5lndcEZOitHTtNCjv0xyBZm 2tIMPNuzjsmhDYAPexZ3FL//2wmUspO8IFgV6dtxQ/PeEMMA3KgqlbbC1j+Qa3bb bP6MvPJwNQzcmRk13NfIRmPVNnGuV/u3gm3c-----END CERTIFICATE-----' COMMENT 'GOOGLE_CERT'; --DROP CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>;Now you can add the certificate to the PSE. Execute the following to retrieve the certificate ID.
SQLCopySELECT CERTIFICATE_ID FROM CERTIFICATES WHERE COMMENT = 'GOOGLE_CERT'; --CERTIFICATE_IDAdd the certificate ID (ex: 123456) from the previous statement into
<CERTIFICATE_ID>. Set the purpose to remote source.SQLCopyALTER PSE HTTPS ADD CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>; --ALTER PSE HTTPS DROP CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>; SET PSE HTTPS PURPOSE REMOTE SOURCE; SELECT * FROM PSE_CERTIFICATES;The above commands create a personal security environment (PSE), create a certificate, add the certificate to the PSE, and set the purpose to remote source.
The GTS Root R1 certificate used above was downloaded from Google Trust Services’ Repository under Download CA certificates > Root CAs >. It was downloaded in the .PEM format.
Additional details can be found at Certificate Management in SAP HANA Cloud.
-
Run the following commands within the SQL console to perform an export using a Google Cloud Storage bucket.
There are two ways to use the export commands as shown below.
SQLCopy--Uses the previously stored credential --EXPORT INTO PARQUET FILE 'gs://<bucket>/<objectKey>' FROM MAINTENANCE WITH CREDENTIAL 'GoogleCloud'; EXPORT INTO PARQUET FILE 'gs://hc-storage-bucket/maintenance.parquet' FROM MAINTENANCE WITH CREDENTIAL 'GoogleCloud'; --Uses the private key as part of the SQL statement --EXPORT INTO PARQUET FILE 'gs://<client_email>:<private_key>@<bucket>/<object_id>' FROM MAINTENANCE; EXPORT INTO PARQUET FILE 'gs://hc-service-account@hc-storage-proj.iam.gserviceaccount.com:-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----MIIEv...-----END PRIVATE KEY-----@hc-storage-bucket/maintenance2.parquet' FROM MAINTENANCE;An alternative to the above SQL commands is to use the Export Data Wizard. The Wizard can be accessed by right clicking a table or view and choosing Export Data. When using the export wizard, the “gs://” prefix is not needed when specifying the GCS Path.

-
Verify the export was completed successfully by refreshing your bucket within Google Cloud Console.

-
Enter the SQL statement below to delete the rows in the table. They will be added back in the next sub-step when the import command is shown.
SQLCopyDELETE FROM MAINTENANCE; -
Run the following commands within the SQL console to perform an import using a Google Cloud Storage bucket.
SQLCopy--Uses the previously stored credential --IMPORT FROM PARQUET FILE 'gs://<bucket>/<objectKey>' WITH CREDENTIAL 'GoogleCloud'; IMPORT FROM PARQUET FILE 'gs://hc-storage-bucket/maintenance.parquet' INTO MAINTENANCE WITH FAIL ON INVALID DATA CREDENTIAL 'GoogleCloud'; --Uses the private key as part of the SQL statement --IMPORT FROM PARQUET FILE 'gs://<client_email>:<private_key>@<bucket>/<object_id>' INTO MAINTENANCE WITH FAIL ON INVALID DATA; IMPORT FROM PARQUET FILE 'gs://hc-service-account@hc-storage-proj.iam.gserviceaccount.com:-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----MIIEvg...-----END PRIVATE KEY-----@hc-storage-bucket/maintenance2.parquet' INTO MAINTENANCE WITH FAIL ON INVALID DATA;
For additional details see the topic Importing and Exporting Data in the SAP HANA Cloud Administration Guide.
-
- Step 6
The following tables list the different options available in the SAP HANA database explorer to export and import catalog objects.
Methods to export catalog objects
Method Version Target Format(s) Limitations Export catalog wizard All Local computer CSV, Binary, *Parquet 2 GB max Export catalog wizard SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS CSV, Binary, Parquet ** Export catalog wizard SAP HANA on-premise SAP HANA file system CSV, Binary ** Export statement SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS CSV, Binary, Parquet ** Export statement SAP HANA on-premise HANA file system CSV, Binary data ** Methods to import catalog objects
Method Version Source Format(s) Limitations Import catalog wizard All Local computer CSV, Binary 2 GB max Import catalog wizard SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS CSV, Binary, Parquet ** Import catalog wizard SAP HANA on-premise SAP HANA file system CSV, Binary 2 GB max per object, ** Import statement SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database S3, Azure, GCS, Alibaba OSS CSV, Binary, Parquet ** Import statement SAP HANA on-premise SAP HANA file system CSV, Binary ** * SAP HANA Cloud, HANA database only
** Max file size in archive is 8 GB (SAP Note 2907201).
Similar to the first section, the maintenance table will be exported and re-imported. The export statement and the associated export catalog wizard have additional options, including the ability to include other schema objects such as functions and procedures as well as the option to include the SQL statements to recreate the objects.
-
Right-click on the instance
HC_HDB (USER1)and choose Export Catalog Objects.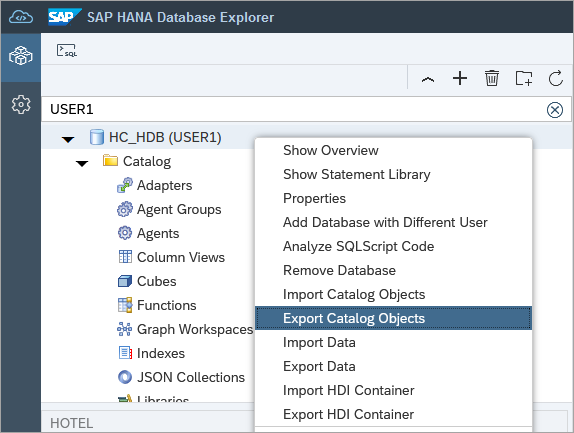
Choose Local Computer for the export location and provide a name for the Local Archive. Click on Add Catalog Objects and search for the table Maintenance. Select an export format such as CSV and press Export.

Examine the available export format options.

Binary Raw is the binary format for SAP HANA Cloud and Binary Data is the format option for SAP HANA as a Service and SAP HANA on-premise.
-
The archive file contains the SQL to recreate the table as well as the data of the table, as shown below.

-
Enter the SQL statement below to drop the table. It will be added back in the next sub-step.
SQLCopyDROP TABLE MAINTENANCE; -
Right-click on the instance
HC_HDB (USER1)and choose Import Catalog.
Browse to the previously downloaded .tar.gz file and complete the wizard. You can also rename the schema, if desired.

The contents of the maintenance table should now be the same as it was before the previously executed drop statement.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM MAINTENANCE;
-
- Step 7
The following steps walk through the process of using Microsoft Azure storage service as a target for an export catalog operation.
-
Log in to the Microsoft Azure Portal.
-
Create a resource group.

-
Create a storage Service

-
Create a blob container.
-
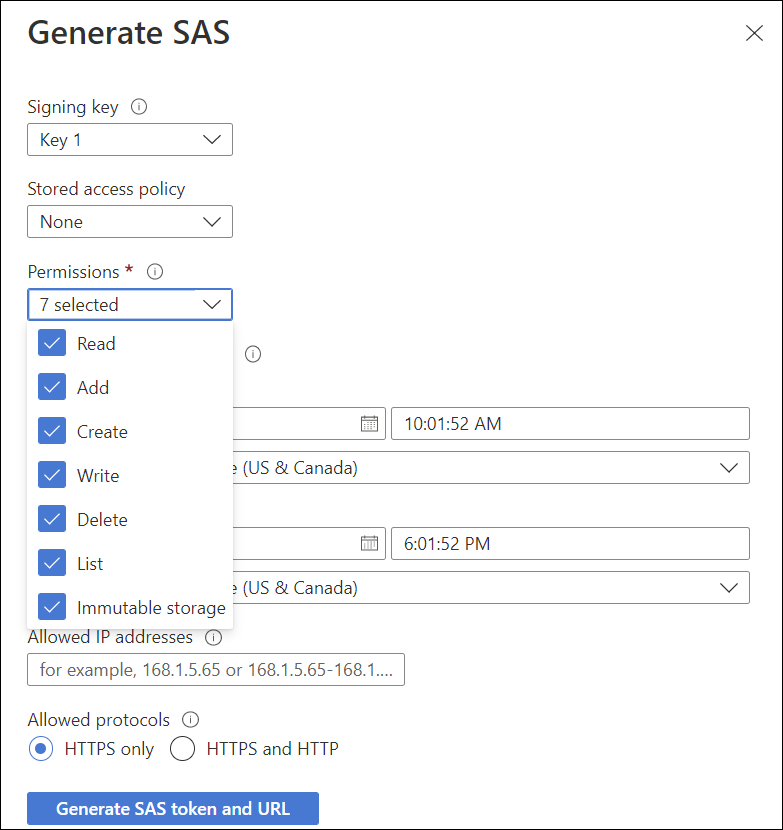
Generate an API key.

Specify that the permissions and the expiry time.
Copy the generated query string and paste it into a text editor. This will be used in step 6.

-
Create Credentials (Recommended)
Execute the following SQL to store the storage account and shared access signature (SAS) as a credential in the database. An example of
<storage_account_name>isdanstestsa.SQLCopyCREATE CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHANAIMPORTEXPORT' PURPOSE 'Azure' TYPE 'PASSWORD' USING 'user=<storage_account_name>;password=<Blob_SAS_token>'; SELECT * FROM CREDENTIALS; --DROP CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHANAIMPORTEXPORT' PURPOSE 'Azure' TYPE 'PASSWORD'; -
In the SAP HANA database explorer, add the certificate used by Microsoft to the HANA Cloud PSE. Open your SQL console within SAP HANA database explorer and run the following commands to create a certificate.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM PSES; CREATE PSE HTTPS; SELECT SUBJECT_COMMON_NAME, CERTIFICATE_ID, COMMENT, CERTIFICATE FROM CERTIFICATES; CREATE CERTIFICATE FROM '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----MIIDdzCCAl+gAwIBAgIEAgAAuTANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADBaMQswCQYDVQQGEwJJ RTESMBAGA1UEChMJQmFsdGltb3JlMRMwEQYDVQQLEwpDeWJlclRydXN0MSIwIAYD VQQDExlCYWx0aW1vcmUgQ3liZXJUcnVzdCBSb290MB4XDTAwMDUxMjE4NDYwMFoX DTI1MDUxMjIzNTkwMFowWjELMAkGA1UEBhMCSUUxEjAQBgNVBAoTCUJhbHRpbW9y ZTETMBEGA1UECxMKQ3liZXJUcnVzdDEiMCAGA1UEAxMZQmFsdGltb3JlIEN5YmVy VHJ1c3QgUm9vdDCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBAKMEuyKr mD1X6CZymrV51Cni4eiVgLGw41uOKymaZN+hXe2wCQVt2yguzmKiYv60iNoS6zjr IZ3AQSsBUnuId9Mcj8e6uYi1agnnc+gRQKfRzMpijS3ljwumUNKoUMMo6vWrJYeK mpYcqWe4PwzV9/lSEy/CG9VwcPCPwBLKBsua4dnKM3p31vjsufFoREJIE9LAwqSu XmD+tqYF/LTdB1kC1FkYmGP1pWPgkAx9XbIGevOF6uvUA65ehD5f/xXtabz5OTZy dc93Uk3zyZAsuT3lySNTPx8kmCFcB5kpvcY67Oduhjprl3RjM71oGDHweI12v/ye jl0qhqdNkNwnGjkCAwEAAaNFMEMwHQYDVR0OBBYEFOWdWTCCR1jMrPoIVDaGezq1 BE3wMBIGA1UdEwEB/wQIMAYBAf8CAQMwDgYDVR0PAQH/BAQDAgEGMA0GCSqGSIb3 DQEBBQUAA4IBAQCFDF2O5G9RaEIFoN27TyclhAO992T9Ldcw46QQF+vaKSm2eT92 9hkTI7gQCvlYpNRhcL0EYWoSihfVCr3FvDB81ukMJY2GQE/szKN+OMY3EU/t3Wgx jkzSswF07r51XgdIGn9w/xZchMB5hbgF/X++ZRGjD8ACtPhSNzkE1akxehi/oCr0 Epn3o0WC4zxe9Z2etciefC7IpJ5OCBRLbf1wbWsaY71k5h+3zvDyny67G7fyUIhz ksLi4xaNmjICq44Y3ekQEe5+NauQrz4wlHrQMz2nZQ/1/I6eYs9HRCwBXbsdtTLS R9I4LtD+gdwyah617jzV/OeBHRnDJELqYzmp-----END CERTIFICATE-----' COMMENT 'Azure'; --DROP CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>;Now you can add the certificate to the PSE. Execute the following to retrieve the certificate ID.
SQLCopySELECT CERTIFICATE_ID FROM CERTIFICATES WHERE COMMENT = 'Azure';Add the certificate ID (ex: 123456) from the previous statement into
<CERTIFICATE_ID>. Set the purpose to remote source.SQLCopyALTER PSE HTTPS ADD CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>; --ALTER PSE HTTPS DROP CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>; SET PSE HTTPS PURPOSE REMOTE SOURCE; SELECT * FROM PSE_CERTIFICATES;Additional details can be found at Certificate Management in SAP HANA Cloud.
The certificate string above is from the root certificate used for the Azure Portal.

-
Start the export catalog wizard and export the maintenance table to the storage service.

Alternatively, you can use a Secret Key as a Credential (optional).
The Azure Path is of the format:
<Storage Account Name>:<generated shared access string>@<Container Name>/<File Name>An example string is shown below:
danstestsa:sp=racwdl&st=2021-01-09T13:00:46Z&se=2021-01-10T13:00:46Z&sv=2019-12-12&sr=c&sig=TP%2BVYhcvSPDc4DZxcls6vN%2BCLHDNagedbei2IuEZsWU%3D@myblobcontainer/maintenance
Pressing the Compose button shows the parsed Azure path.

After the Export button is pressed, the results can be seen in the Azure Portal.

The equivalent SQL statement is shown below:
SQLCopyEXPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET INTO 'azure://dansblobcont/maintenance/' WITH CREDENTIAL 'Azure';' -
Enter the SQL statement below to drop the table. It will be added back in the next step.
SQLCopyDROP TABLE MAINTENANCE; -
Import the table using the import catalog objects wizard.

The contents of the maintenance table should now be the same as it was before the previously executed drop statement.
The equivalent SQL statement is shown below:
SQLCopyIMPORT MAINTENANCE FROM 'azure://danstestsa:sp=racwdl&st=2021-01-09T13:00:46Z&se=2021-01-10T13:00:46Z&sv=2019-12-12&sr=c&sig=TP%2BVYhcvSPDc4DZxcls6vN%2BCLHDNagedbei2IuEZsWU%3D@myblobcontainer/maintenance' WITH REPLACE;For additional details see the topic Importing and Exporting Data in the SAP HANA Cloud Administration Guide.
-
- Step 8
The following steps walk through the process of AWS S3 storage service as a target for an export catalog operation.
-
Log in to the AWS S3 Management Console.
-
Navigate to the S3 storage service.

-
Create an AWS bucket.

Provide a unique bucket name, choose your AWS region, and finish creating the bucket.

-
Create a IAM User.
It is recommended that you create an IAM User instead of using the root account to manage the S3 bucket. If you already have an existing IAM User, then feel free to skip this step, and go ahead and generate an access key and secret key for an existing IAM User.
To create an IAM User, begin by logging in with your root credentials, and navigate to the Security Credentials tab.

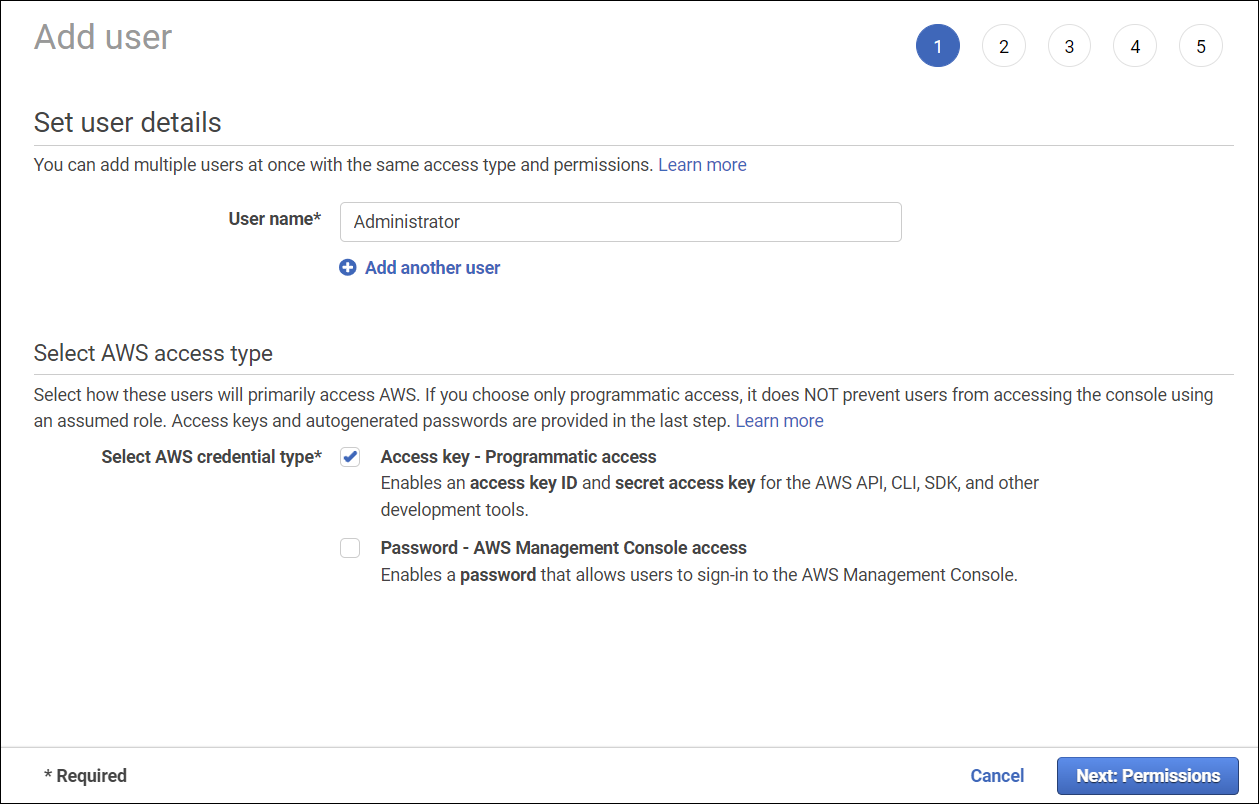
Select add users.

Specify user details such as User name and select the AWS credential type.
Select Attach existing policies directly and provide full Amazon S3 Access.

Finish creating the user.

Copy and Save the Access key ID and Secret access key, as it will be required in step 5.

-
Create Credentials (Recommended)
Execute the following SQL to store the access key and secret key as a credential in the database.
SQLCopyCREATE CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHANAIMPORTEXPORT' PURPOSE 'AWS' TYPE 'PASSWORD' USING 'user=<access_key>;password=<secret_key>'; SELECT * FROM CREDENTIALS; --DROP CREDENTIAL FOR COMPONENT 'SAPHANAIMPORTEXPORT' PURPOSE 'AWS' TYPE 'PASSWORD';Use the
access_keyandsecret_keyfrom Step 3. Additionally, if you didn’t follow step 3 as you have an existing IAM user, then generate an access key and secret key for an existing IAM User.Additional details can be found at CREATE CREDENTIAL Statement and CREDENTIALS System View.
-
In the SAP HANA database explorer, create the certificate used by AWS to the HANA Cloud PSE.
The certificate below is the Amazon Root CA 1 from Amazon Trust Services.
SQLCopySELECT * FROM PSES; CREATE PSE HTTPS; SELECT SUBJECT_COMMON_NAME, CERTIFICATE_ID, COMMENT, CERTIFICATE FROM CERTIFICATES; CREATE CERTIFICATE FROM '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIDQTCCAimgAwIBAgITBmyfz5m/jAo54vB4ikPmljZbyjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsF ADA5MQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEPMA0GA1UEChMGQW1hem9uMRkwFwYDVQQDExBBbWF6 b24gUm9vdCBDQSAxMB4XDTE1MDUyNjAwMDAwMFoXDTM4MDExNzAwMDAwMFowOTEL MAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxDzANBgNVBAoTBkFtYXpvbjEZMBcGA1UEAxMQQW1hem9uIFJv b3QgQ0EgMTCCASIwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEBBQADggEPADCCAQoCggEBALJ4gHHKeNXj ca9HgFB0fW7Y14h29Jlo91ghYPl0hAEvrAIthtOgQ3pOsqTQNroBvo3bSMgHFzZM 9O6II8c+6zf1tRn4SWiw3te5djgdYZ6k/oI2peVKVuRF4fn9tBb6dNqcmzU5L/qw IFAGbHrQgLKm+a/sRxmPUDgH3KKHOVj4utWp+UhnMJbulHheb4mjUcAwhmahRWa6 VOujw5H5SNz/0egwLX0tdHA114gk957EWW67c4cX8jJGKLhD+rcdqsq08p8kDi1L 93FcXmn/6pUCyziKrlA4b9v7LWIbxcceVOF34GfID5yHI9Y/QCB/IIDEgEw+OyQm jgSubJrIqg0CAwEAAaNCMEAwDwYDVR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zAOBgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMC AYYwHQYDVR0OBBYEFIQYzIU07LwMlJQuCFmcx7IQTgoIMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUA A4IBAQCY8jdaQZChGsV2USggNiMOruYou6r4lK5IpDB/G/wkjUu0yKGX9rbxenDI U5PMCCjjmCXPI6T53iHTfIUJrU6adTrCC2qJeHZERxhlbI1Bjjt/msv0tadQ1wUs N+gDS63pYaACbvXy8MWy7Vu33PqUXHeeE6V/Uq2V8viTO96LXFvKWlJbYK8U90vv o/ufQJVtMVT8QtPHRh8jrdkPSHCa2XV4cdFyQzR1bldZwgJcJmApzyMZFo6IQ6XU 5MsI+yMRQ+hDKXJioaldXgjUkK642M4UwtBV8ob2xJNDd2ZhwLnoQdeXeGADbkpy rqXRfboQnoZsG4q5WTP468SQvvG5-----END CERTIFICATE-----' COMMENT 'S3';Now you can add the certificate to the PSE. Execute the following to retrieve the certificate ID.
SQLCopySELECT CERTIFICATE_ID FROM CERTIFICATES WHERE COMMENT = 'S3';Add the certificate ID (ex: 123456) from the previous statement into
<CERTIFICATE_ID>. Set the purpose to remote source.SQLCopySELECT * FROM PSE_CERTIFICATES; ALTER PSE HTTPS ADD CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>; --ALTER PSE HTTPS DROP CERTIFICATE <CERTIFICATE_ID>; SET PSE HTTPS PURPOSE REMOTE SOURCE;Additional details can be found at Certificate Management in SAP HANA Cloud.
-
Start the export catalog wizard and export the maintenance table to the storage service.
The AWS S3 Path (in the Export Catalog Objects Wizard) is of the format:
<access_key>:<secret_key>@<bucket_name>/<object_id>Use the
access_keyandsecret_keyfrom Step 3. Additionally, if you didn’t follow step 3 as you have an existing IAM user, then generate an access key and secret key for an existing IAM User.An example string is shown below:
AKIA3JHRPYB6KY3LSI76:dW9q+KxA0rgtaoBY3MnAAQIS96ypVEDvgxE8rIpt@maitrysawsbucket/maintenance
Alternatively, you can use a Secret Key as a Credential (optional)

Pressing the Compose button shows the parsed AWS S3 path.

After the Export button is pressed, the results can be seen in the AWS S3 Console.

The equivalent SQL statement is shown below:
SQLCopy--EXPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET INTO 's3-<region>://<access_key>:<secret_key>@<bucket>/<object_id>' WITH REPLACE; EXPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET INTO 's3-us-east-1://AKIA3JHRPYB6KY3LSI76:dW9q+KxA0rgtaoBY3MnAAQIS96ypVEDvgxE8rIpt@maitrysawsbucket/maintenance' WITH REPLACE;The previously stored credentials can be used for export using SQL:
SQLCopy--EXPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET INTO 's3-<region>://<bucket>/<objectKey>' WITH CREDENTIAL 'AWS'; EXPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET INTO 's3-us-east-1://maitrysawsbucket/maintenance' WITH CREDENTIAL 'AWS';An error regarding an invalid SSL certificate indicates an incorrect SSL certificate is being used. Additionally, if MFA (Multi-factor Authentication) is enabled, then the export may fail, so ensure that MFA is disabled before exporting.
-
Enter the SQL statement below to drop the table. It will be added back in the next step.
SQLCopyDROP TABLE MAINTENANCE; -
Import the table using the import catalog objects wizard.
The AWS S3 Path (in the Import Catalog Objects Wizard) is of the format:
<access_key>:<secret_key>@<bucket_name>/<object_id>An example string is shown below:
AKIA3JHRPYB6KY3LSI76:dW9q+KxA0rgtaoBY3MnAAQIS96ypVEDvgxE8rIpt@maitrysawsbucket/maintenanceSelect Load to load the catalog object in the wizard.

The contents of the maintenance table should now be the same as it was before the previously executed drop statement.
The equivalent SQL statement is shown below:
SQLCopy--IMPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET FROM 's3-<region>://<access_key>:<secret_key>@<bucket>/<object_id>' WITH REPLACE; IMPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET FROM 's3-us-east-1://AKIA3JHRPYB6KY3LSI76:dW9q+KxA0rgtaoBY3MnAAQIS96ypVEDvgxE8rIpt@maitrysawsbucket/maintenance' WITH REPLACE;Alternatively, the previously stored credentials can be used for import:
SQLCopy--EXPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET FROM 's3-<region>://<bucket>/<objectKey>' WITH CREDENTIAL 'AWS'; IMPORT MAINTENANCE AS PARQUET FROM 's3-us-east-1://maitrysawsbucket/maintenance' WITH CREDENTIAL 'AWS';For additional details see the topic Importing and Exporting Data in the SAP HANA Cloud Administration Guide.
-
- Step 9
Congratulations! You have imported and exported data and catalog objects.
Which of the following statements are true?
- Export and import data
- Use cloud storage services for export and import (optional)
- Use data lake Files for export and import from an SAP HANA Cloud, SAP HANA database (optional)
- Use data lake Files for export and import from an SAP HANA Cloud, data lake Relational Engine database (optional)
- Use Google Cloud Storage (GCS) for data exports and imports (optional)
- Export and import schema or catalog objects
- Use Azure cloud storage for exports and imports of catalog objects (optional)
- Use Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3 for exports and imports of catalog objects (optional)
- Knowledge check