Connect Using the SAP HANA Node.js Interface
- How to install Node.js and the SAP HANA client Node.js driver
- How to create a Node.js application that queries a SAP HANA database
- How to use both the synchronous and asynchronous driver interfaces
Prerequisites
- You have completed the first 3 tutorials in this mission.
Node.js provides a JavaScript runtime outside of the browser and uses an asynchronous event driven programming model. For more details, see Introduction to Node.js.
- Step 1
Ensure you have Node.js installed and check its version. Enter the following command:
ShellCopynode -vIf Node.js is installed, the currently installed version is returned, such as v20.10.0.
If Node.js is not installed, download the long-term support (LTS) version of Node.js from Download Node.js.
If an install for Node.js is not provided on Linux, you may choose to install it via a package manager. For more details, please navigate to this link.
During the installation, there is no need to install tools for native modules.

The SAP HANA client provides a 32-bit and a 64-bit install, as does Node.js. The Node.js driver provided with the SAP HANA client is available for 64-bit only. For further details on supported versions, see SAP Note 3165810 - SAP HANA Client Supported Platforms.
Another option is to use a docker image that contains Node.js as shown below.
ShellCopydocker run -it --name=nodealpine node:alpine /bin/bash - Step 2
Node.js packages are available using NPM, which is the standard package manager for Node.js.
-
Enter
hana client, and click Search.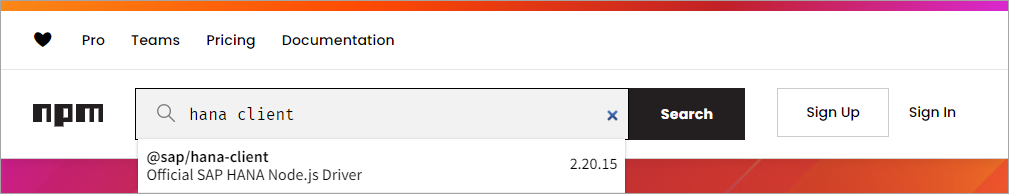
The page for the SAP HANA Node.js package on npm is shown below.

It contains additional sample code, a weekly download counter, information about previous versions and the command to install the package using the npm command line interface (
cli). -
Create a folder named
nodeand enter the newly created directory.Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copymkdir %HOMEPATH%\HANAClientsTutorial\node cd %HOMEPATH%\HANAClientsTutorial\nodeShell (Linux or Mac)Copymkdir -p $HOME/HANAClientsTutorial/node cd $HOME/HANAClientsTutorial/node -
Initialize the project and install the
hana-clientdriver from NPM.ShellCopynpm init -y npm install @sap/hana-clientThe
hana-clientdriver contains native libraries as shown below.
When installed using NPM, the native libraries for all available platforms are downloaded. The following environment variable can be used to remove the other platforms reducing the size of the project. For additional details, see Node.js Environment Variables.
Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copyset HDB_NODE_PLATFORM_CLEAN=1 npm uninstall @sap/hana-client npm install @sap/hana-clientShell (Linux or Mac)Copyexport HDB_NODE_PLATFORM_CLEAN=1 npm uninstall @sap/hana-client npm install @sap/hana-client
The hana-client driver is also available from the HANA client install folder. The install location was set during the install.
Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copycd C:\SAP\hdbclient\node npm install cd %HOMEPATH%\HANAClientsTutorial\node npm install C:\SAP\hdbclient\nodeIf you encounter an error about permissions, on Microsoft Windows, run or open the command prompt as an administrator, or use
sudoon Linux or Mac. -
The following command lists the Node.js modules that are now installed locally into the
HANAClientsTutorial\nodefolder.ShellCopynpm list
Some Tips
At this point, the SAP HANA client module has been installed into the
HANAClientsTutorials\node\node_modulesfolder and added as a dependency in thepackages.jsonfile. The following is some extra optional information on NPM.
Node.js modules can also be installed globally. To see the list of Node.js modules installed globally enter the following command.
The depth parameter can be used to specify the number of levels to show when displaying module dependencies. By setting depth=x, a tree-structure is outputted that shows modules that are x levels below the top-level module.
ShellCopynpm list -g npm list -g --depth=0Command line help for NPM is available. A few examples of this are shown below.
ShellCopynpm help npm help listAdditional information can be found out for a module, such as the debug module, via the info command.
ShellCopynpm info @sap/hana-clientThe following commands can be used to view the latest available version of a package, remove a package, add a specific version of a package and then update it to the latest version.
ShellCopynpm view @sap/hana-client version npm uninstall @sap/hana-client npm install @sap/hana-client@2.12.25 npm list @sap/hana-client npm update @sap/hana-client npm list @sap/hana-client -
- Step 3
-
Open a file named
nodeQuery.jsin an editor.Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copynotepad nodeQuery.jsSubstitute
picobelow for your preferred text editor.Shell (Linux or Mac)Copypico nodeQuery.js -
Add the code below to
nodeQuery.js. Note that the values for host, port, user name and password are provided by the previously configuredhdbuserstorekey USER1UserKey. Save the file when finished.JavaScriptCopy'use strict'; const { PerformanceObserver, performance } = require('perf_hooks'); var util = require('util'); var hana = require('@sap/hana-client'); var connOptions = { //Option 1, retrieve the connection parameters from the hdbuserstore serverNode: '@USER1UserKey', //host, port, uid, and pwd retrieved from hdbuserstore //Option 2, specify the connection parameters //serverNode: 'host:port', //UID: 'USER1', //PWD: 'Password1', //Additional parameters //As of 2.7 trace info can be directed to stdout or stderr //traceFile: 'stdout', //traceOptions: 'sql=warning', //As of SAP HANA client 2.6, connections on port 443 enable encryption by default (HANA Cloud). //encrypt: 'true', //Must be set to true when connecting to HANA as a Service sslValidateCertificate: 'false', //Must be set to false when connecting to an SAP HANA, express edition instance that uses a self-signed certificate. //For encrypted connections, the default crypto provider is mscrypto on Windows or openSSL on Linux or macos //To use the SAP crypto provider, uncomment the below line. //sslCryptoProvider: 'commoncrypto', //As of SAP HANA client 2.6 for OpenSSL connections, the following settings can be ignored as root certificates are read from the default OS location. //ssltruststore: '/home/dan/.ssl/trust.pem', //Used to specify where the trust store is located //Alternatively provide the contents of the certificate directly (DigiCertGlobalRootCA.pem) //DigiCert Global Root CA: https://cacerts.digicert.com/DigiCertGlobalRootCA.crt.pem used for SAP HANA cloud //on-premise cert can be retrieved using openssl s_client -connect localhost:39015 //This option is not supported with the mscrypto provider (the default provider on Windows) //ssltruststore: '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----MIIDrzCCApegAwIBAgIQCDvgVpBCRrGhdWrJWZHHSjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQUFADBhMQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEVMBMGA1UEChMMRGlnaUNlcnQgSW5jMRkwFwYDVQQLExB3d3cuZGlnaWNlcnQuY29tMSAwHgYDVQQDExdEaWdpQ2VydCBHbG9iYWwgUm9vdCBDQTAeFw0wNjExMTAwMDAwMDBaFw0zMTExMTAwMDAwMDBaMGExCzAJBgNVBAYTAlVTMRUwEwYDVQQKEwxEaWdpQ2VydCBJbmMxGTAXBgNVBAsTEHd3dy5kaWdpY2VydC5jb20xIDAeBgNVBAMTF0RpZ2lDZXJ0IEdsb2JhbCBSb290IENBMIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEA4jvhEXLeqKTTo1eqUKKPC3eQyaKl7hLOllsBCSDMAZOnTjC3U/dDxGkAV53ijSLdhwZAAIEJzs4bg7/fzTtxRuLWZscFs3YnFo97nh6Vfe63SKMI2tavegw5BmV/Sl0fvBf4q77uKNd0f3p4mVmFaG5cIzJLv07A6Fpt43C/dxC//AH2hdmoRBBYMql1GNXRor5H4idq9Joz+EkIYIvUX7Q6hL+hqkpMfT7PT19sdl6gSzeRntwi5m3OFBqOasv+zbMUZBfHWymeMr/y7vrTC0LUq7dBMtoM1O/4gdW7jVg/tRvoSSiicNoxBN33shbyTApOB6jtSj1etX+jkMOvJwIDAQABo2MwYTAOBgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMCAYYwDwYDVR0TAQH/BAUwAwEB/zAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUA95QNVbRTLtm8KPiGxvDl7I90VUwHwYDVR0jBBgwFoAUA95QNVbRTLtm8KPiGxvDl7I90VUwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEFBQADggEBAMucN6pIExIK+t1EnE9SsPTfrgT1eXkIoyQY/EsrhMAtudXH/vTBH1jLuG2cenTnmCmrEbXjcKChzUyImZOMkXDiqw8cvpOp/2PV5Adg06O/nVsJ8dWO41P0jmP6P6fbtGbfYmbW0W5BjfIttep3Sp+dWOIrWcBAI+0tKIJFPnlUkiaY4IBIqDfv8NZ5YBberOgOzW6sRBc4L0na4UU+Krk2U886UAb3LujEV0lsYSEY1QSteDwsOoBrp+uvFRTp2InBuThs4pFsiv9kuXclVzDAGySj4dzp30d8tbQkCAUw7C29C79Fv1C5qfPrmAESrciIxpg0X40KPMbp1ZWVbd4=-----END CERTIFICATE-----' }; //Synchronous example querying a table var connection = hana.createConnection(); //As of 2.9, tracing can be directed to a callback /* var traceCB = function (buf) { console.log(buf); }; connection.onTrace("sql=error,api=debug,OutBufferSize=64k", traceCB); */ connection.connect(connOptions); //connection.onTrace("", null); //disables callback tracing for the rest of the program var sql = 'SELECT TITLE, FIRSTNAME, NAME FROM HOTELS.CUSTOMER;'; var t0 = performance.now(); var result = connection.exec(sql); console.log(util.inspect(result, { colors: false })); var t1 = performance.now(); console.log("time in ms " + (t1 - t0)); connection.disconnect(); -
Run the app.
ShellCopynode nodeQuery.js
Note the above app makes use of some of the SAP HANA client Node.js driver methods, such as connect, exec and disconnect.
Notice in the documentation that the above methods support being called in a synchronous or asynchronous manner. Two examples showing the drivers methods being used asynchronously are shown in the next two steps.
-
To enable debug logging of the SAP HANA Node.js client, enter the following command and then rerun the app.
Command Prompt (Microsoft Windows)Copyset DEBUG=* node nodeQuery.jsPowershell (Microsoft Windows)Copy$env:DEBUG='*' node nodeQuery.jsShell (Linux or Mac)Copyexport DEBUG=* node nodeQuery.js
The value of the environment variable DEBUG can be seen and removed with the commands below.
Command Prompt (Microsoft Windows)Copyset DEBUG set DEBUG= set DEBUGPowershell (Microsoft Windows)Copy$env:DEBUG $env:DEBUG='*' Remove-Item Env:DEBUGShell (Linux or Mac)Copyprintenv | grep DEBUG unset DEBUG printenv | grep DEBUG
-
- Step 4
Connection pooling can improve performance when making multiple, brief connections to the SAP HANA database. The following sample makes two connections one after another without using a connection pool and then using a connection pool. It demonstrates how the time taken to make a connection with a connection retrieved from a pool is significantly shorter.
-
Open a file named
nodeQueryConnectionPool.jsin an editor.Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copynotepad nodeQueryConnectionPool.jsSubstitute
picobelow for your preferred text editor.Shell (Linux or Mac)Copypico nodeQueryConnectionPool.js -
Add the code below to
nodeQueryConnectionPool.js. Note that the values for host, port, user name and password are provided by the previously configuredhdbuserstorekey USER1UserKey. Save the file when finished.JavaScriptCopy'use strict'; const { PerformanceObserver, performance } = require('perf_hooks'); var util = require('util'); var hana = require('@sap/hana-client'); var connOptions = { //Option 1, retrieve the connection parameters from the hdbuserstore serverNode: '@USER1UserKey' //host, port, uid, and pwd retrieved from hdbuserstore //Option 2, specify the connection parameters //serverNode: 'host:port', //UID: 'USER1', //PWD: 'Password1', }; var poolProperties = { poolCapacity: 10, //max # of connections in the pool waiting to be used maxConnectedOrPooled: 20, //max # of connections in the pool + the # of connections in use pingCheck: false, allowSwitchUser: true, //requires SAP HANA client 2.17 maxPooledIdleTime: 3600, //1 hour (in seconds) } var pool = null; queryTable(false, "1st Run"); queryTable(false, "2nd Run"); queryTable(true, "1st Run"); queryTable(true, "2nd Run"); queryTable(true, "3rd Run", true); //change user console.log("Connections in use :" + pool.getInUseCount()); console.log("Connections in the pool :" + pool.getPooledCount()); //Creates two connections either using connection pooling or not //Displays timing information function queryTable(usePool, run, user2) { var t0 = performance.now() var connection = null; if (usePool) { //use the connection pool var t0 = performance.now(); if (pool === null) { pool = hana.createPool(connOptions, poolProperties); //create a connection pool } if (user2) { //example of changing the user connection = pool.getConnection('USER2','Password2'); //Requires 2.17 of the SAP HANA client } else { connection = pool.getConnection(); //get a connection from the pool } var t1 = performance.now(); } else { //don't use the connection pool connection = hana.createConnection(); connection.connect(connOptions); var t1 = performance.now(); } var t2 = performance.now(); var sql = 'select CURRENT_USER FROM DUMMY;'; var result = connection.exec(sql); var t3 = performance.now(); var t4 = performance.now(); console.log(util.inspect(result, { colors: false })); var t5 = performance.now(); var t6 = performance.now(); connection.disconnect(); //returns connection to the pool var t7 = performance.now(); console.log("Connection Pool Enabled: " + usePool + " " + run); console.log("====================================="); console.log("Connection time in ms: " + (t1 - t0)); console.log("Query time in ms " + (t3 - t2)); console.log("Display time in ms: " + (t5 - t4)); console.log("Disconnect time in ms: " + (t7 - t6)); console.log("Total time in ms: " + (t7 - t0) + "\n"); } -
Run the app.
ShellCopynode nodeQueryConnectionPool.jsNotice below that the time taken to establish a connection is approx 900 ms which but becomes almost instantaneous when the connection pool is used or about 85 ms when a connection from the pool requires changing the user.

See Node.js Connection Pooling for additional details. The example above uses a new API that was added in the 2.17 release.
-
- Step 5
Asynchronous programming enables non-blocking code execution which is demonstrated in the below example.
-
Open a file named
nodeQueryCallback.jsin an editor.Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copynotepad nodeQueryCallback.jsSubstitute
picobelow for your preferred text editor.Shell (Linux or Mac)Copypico nodeQueryCallback.js -
Add the code below to
nodeQueryCallback.js. Note that the values for host, port, user name and password are provided by the previously configuredhdbuserstorekey USER1UserKey. Save the file when finished.JavaScriptCopy'use strict'; var util = require('util'); var hana = require('@sap/hana-client'); var connOptions = { //Option 1, retrieve the connection parameters from the hdbuserstore serverNode: '@USER1UserKey', //host, port, uid, and pwd retrieved from hdbuserstore //Option 2, specify the connection parameters //serverNode: 'host:port', //UID: 'USER1', //PWD: 'Password1', sslValidateCertificate: 'false', //Must be set to false when connecting to an SAP HANA, express edition instance that uses a self-signed certificate. }; //Asynchronous example calling a stored procedure with callbacks var connection = hana.createConnection(); connection.connect(connOptions, function(err) { if (err) { return console.error(err); } //Prepared statement example const statement = connection.prepare('CALL HOTELS.SHOW_RESERVATIONS(?,?)'); const parameters = [11, '2020-12-24']; var results = statement.execQuery(parameters, function(err, results) { if (err) { return console.error(err); } processResults(results, function(err) { if (err) { return console.error(err); } results.close(function(err) { if (err) { return console.error(err); } statement.drop(function(err) { if (err) { return console.error(err); } return connection.disconnect(function(err) { if (err) { return console.error(err); } }); }); }); }); }); }); function processResults(results, cb) { results.next(function (err, hasValues) { if (err) { return console.error(err); } if (hasValues) { results.getValues(function (err, row) { console.log(util.inspect(row, { colors: false })); processResults(results, cb); }); } else { return cb(); } }); } -
Run the app.
ShellCopynode nodeQueryCallback.js
Notice that asynchronous method calls use callback functions.
-
- Step 6
The Node.js driver for the SAP HANA client added support for promises in the 2.11 release. The following example demonstrates this. Notice that there is less nesting of code then the previous example.
-
Open a file named
nodeQueryPromise.jsin an editor.Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copynotepad nodeQueryPromise.jsSubstitute
picobelow for your preferred text editor.Shell (Linux or Mac)Copypico nodeQueryPromise.js -
Add the code below to
nodeQueryPromise.js. Note that the values for host, port, user name and password are provided by the previously configuredhdbuserstorekey USER1UserKey. Save the file when finished.JavaScriptCopy'use strict'; var util = require('util'); var hana = require('@sap/hana-client'); var PromiseModule = require('@sap/hana-client/extension/Promise.js'); var connOptions = { //Option 1, retrieve the connection parameters from the hdbuserstore serverNode: '@USER1UserKey', //host, port, uid, and pwd retrieved from hdbuserstore //Option 2, specify the connection parameters //serverNode: 'host:port', //UID: 'USER1', //PWD: 'Password1', sslValidateCertificate: 'false', //Must be set to false when connecting to an SAP HANA, express edition instance that uses a self-signed certificate. }; //Asynchronous example calling a stored procedure that uses the promise module var connection = hana.createConnection(); var statement; PromiseModule.connect(connection, connOptions) .then(() => { //Prepared statement example return PromiseModule.prepare(connection, 'CALL HOTELS.SHOW_RESERVATIONS(?,?)'); }) .then((stmt) => { statement = stmt; const parameters = [11, '2020-12-24']; return PromiseModule.executeQuery(stmt, parameters); }) .then((results) => { return processResults(results); }) .then((results) => { return PromiseModule.close(results); }) .then(() => { return PromiseModule.drop(statement); }) .then(() => { PromiseModule.disconnect(connection); }) .catch(err => { console.error(err); }); function processResults(results) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { var done = false; PromiseModule.next(results) .then((hasValues) => { if (hasValues) { return PromiseModule.getValues(results); } else { done = true; } }) .then((values) => { if (done) { resolve(results); } else { console.log(util.inspect(values, { colors: false })); processResults(results) .then((results) => { resolve(results); }); } }) .catch (err => { reject(err); }); }) } -
Run the app.
ShellCopynode nodeQueryPromise.js
The above code makes use of the promise module. Additional details on promises can be found at Using Promises.
-
- Step 7
Visual Studio Code can run and debug a Node.js application. It is a lightweight but powerful source code editor which is available on Windows, macOS and Linux.
-
If required, download Visual Studio Code.
-
In Visual Studio Code, choose File | Add Folder to Workspace and then add the
HANAClientsTutorialfolder.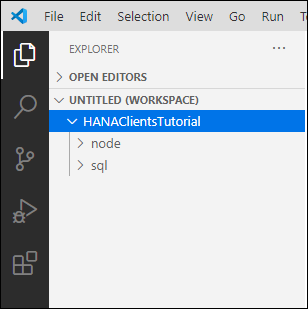
-
Open the file
nodeQuery.js. -
Place a breakpoint inside the
connection.execcallback. Select Run | Start Debugging | Node.js.Notice that the debug view becomes active.
Notice that the program stops running at the breakpoint that was set. Observe the variable values in the leftmost pane. Step through code.

-
- Step 8
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that provides optional types, compile-time checking, and code completion when using a tool such as Visual Studio Code. The following step provides an example of using TypeScript with the SAP HANA client Node.js interface.
-
Examine the interface file which is located at
C:\SAP\hdbclient\node\lib\index.d.tsin SAP HANA client versions 2.16 and higher.
Notice that it contains definitions for the methods of the SAP HANA client Node.js interface. The method
setClientInfowill be highlighted in substep 6. -
Open a file named
nodeQueryTS.jsin an editor.Shell (Microsoft Windows)Copynotepad nodeQueryTS.tsSubstitute
picobelow for your preferred text editor.Shell (Linux or Mac)Copypico nodeQueryTS.ts -
Add the code below to
nodeQueryTS.js. Note that the values for host, port, user name and password are provided by the previously configuredhdbuserstorekey USER1UserKey.JavaScriptCopy"use strict"; import * as hana from '@sap/hana-client'; var connection: hana.Connection = hana.createConnection(); var connOptions: hana.ConnectionOptions = { serverNode: '@USER1UserKey', //host, port, uid, and pwd retrieved from hdbuserstore //serverNode: '123456-7890-400a-8bbd-41097dfd15ae.hana0.prod-us10.hanacloud.ondemand.com:443', //UID: 'USER1', //PWD: 'Password1' }; connection.connect(connOptions); connection.setClientInfo("CURRENT_YEAR", 2023); //should be "2023" console.log("Year session value is " + connection.getClientInfo("CURRENT_YEAR")); var sql1: string = "SELECT TITLE, FIRSTNAME, NAME FROM HOTELS.CUSTOMER WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE ?"; var statement: hana.Statement = connection.prepare(sql1); var result1: hana.ResultSet = statement.executeQuery(['M%']); var moreData: boolean = result1.next(); while (moreData) { var row : {[key: string]: string} = result1.getValues(); console.log(row); moreData = result1.next(); } connection.disconnect(); -
Check if TypeScript is already installed and if not install it.
ShellCopytsc -versionIf the TypeScript is installed, a version value will be returned.

If TypeScript is not installed, it can be installed globally with the below command.
ShellCopynpm install -g typescript -
Add the types module.
First check the Node.js version, determine what modules are in the current project, and what are the available versions of
@types/node.ShellCopynpm info @types/nodeInstall the @types/node module which provides type definitions for Node.js.
ShellCopynpm install @types/node node -v npm list
The major version of Node.js and the
@types/nodeversions should match. If you need to uninstall@types/nodeand install a different version, an example is shown below of the commands to do so.ShellCopynpm uninstall @types/node npm install @types/node@18.15.11 -
Run the TypeScript compiler and notice that it finds an error.
ShellCopytsc nodeQueryTS.ts
-
Open Visual Studio Code. Notice that it also shows the error.

-
On a new line enter
connection.sand notice that code completion is provided for the client interface methods.
Further details on using TypeScript within Visual Studio Code can be found at TypeScript tutorial in Visual Studio Code.
-
Correct the error, compile, and run the app using the following commands. The error can be corrected by changing 2023 to “2023”.
ShellCopytsc nodeQueryTS.ts node nodeQueryTS.js
-
- Step 9
Congratulations! You have created and debugged a Node.js application that connects to and queries an SAP HANA database.
Which of the following statements are true?
- Install Node.js
- Install SAP HANA client for Node.js from NPM
- Create a synchronous Node.js application that queries SAP HANA
- Create a synchronous app that uses a connection pool
- Create an asynchronous app that uses callbacks
- Create an asynchronous app that uses promises
- Debug the application
- Use TypeScript
- Knowledge check