Detailed Query Plan and Indexes
- Accessing a more detailed HTML query plan through SAP HANA Studio.
- Creating indexes on table columns to improve query performance.
- Analyzing the impact of indexes on query plans.
Prerequisites
- Step 1
In addition to the graphical query plan available through the
PlanVizperspective, you can access an even more detailed query plan for the Dynamic Tiering portion of the query. In order to do this we will need to turn on a debug level of tracing.In SAP HANA Studio, go to SAP HANA Administration Console. In the Systems tab on the left, double click on the system you are working with.

After the administration console opens, go to the Trace Configuration tab.

Click on the pencil icon under Database Trace to edit debug level.

A window should pop up where you need to click on the drop-down icon beside INDEXSERVER. Check the box for Show All Components on the bottom left.

You should now be able to see the field
fedtraceunder INDEXSERVER. Alternatively, you can also enter “fedtrace” in the type filter search box to find the field. In this row, click under the System Trace Level and select the option DEBUG and then click Finish.
You need to turn on what level of tracing before you can open the detailed plan for the Dynamic Tiering portion of the query?
- Step 2
In SAP HANA Administration Console, open a new SQL console.

Copy and paste the script below into the SQL console.
sqlCopySELECT 100.00 * SUM(CASE WHEN P_TYPE LIKE 'PROMO%' THEN L_EXTENDEDPRICE * (1 - L_DISCOUNT) ELSE 0 END) / SUM(L_EXTENDEDPRICE * (1 - L_DISCOUNT)) as promo_revenue FROM "TPCH"."LINEITEM_DT", "TPCH"."PART_DT" WHERE L_PARTKEY = P_PARTKEY AND L_SHIPDATE >= '2014-10-01' AND L_SHIPDATE < '2014-11-01';
Right click inside the SQL console, then select Visualize Plan > Execute. You can also press Ctrl + Shift + X.

In SAP HANA Studio, go to SAP HANA Administration Console. In the Systems tab on the left, double click on the system you are working with.

After the administration console opens, go to the Diagnosis Files tab.

The detailed plan file would have your Dynamic Tiering node as host. You can sort the entries by clicking on the Host header. Click on the Modified header to sort the files by modified date. Find the most recent HTML file with the name similar to “
dbo_HANA_ES_###...##.html”. You can also enter “dbo_HANA_ES_*.html” into the Filter box. Right click on the file and select Download… to download the file.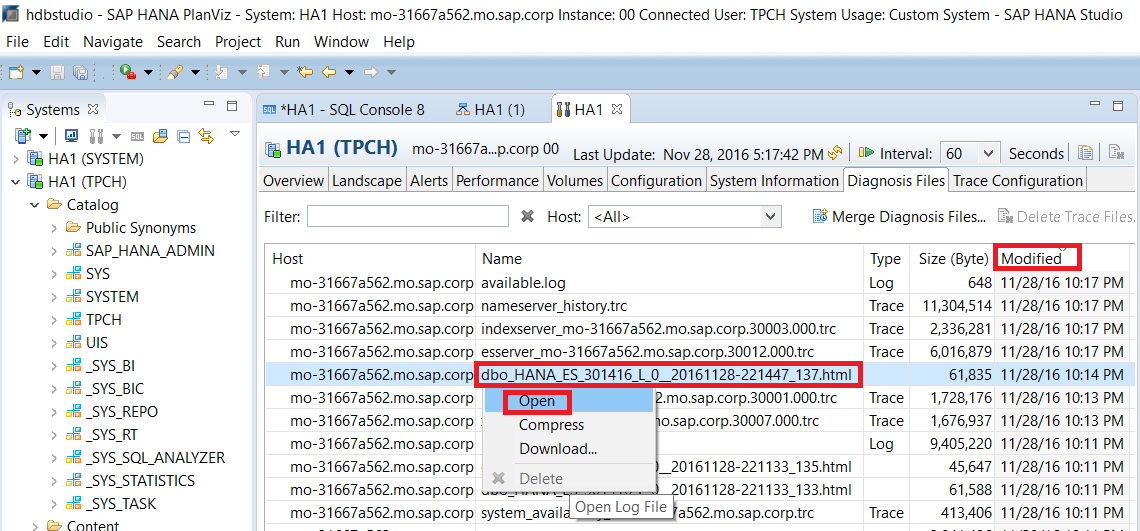
In the “Save As” pop up window, select where you want the file to be saved. Then click Save to save the file.
Navigate to the directory where the detailed query plan file is saved and double click to open it using your default web browser.
You should now see the detailed query plan. Scroll toward the end to find Condition 1 Index.
The highlighted index in the query plan below is the Fast Projection (FP) index. The FP indexes are automatically generated for each column in a Dynamic Tiering table. This FP index optimizes projections and enables certain kinds of search conditions to be evaluated. In the absence of any other index, the query plan will normally reference the FP index for the specific column.

- Step 3
Go to SAP HANA Administration Console and open a new SQL console.
Copy and paste the script into the console. Then run the script to create a new index.
sqlCopyCREATE INDEX L_SHIPDATE_INDEX ON LINEITEM_DT (L_SHIPDATE);Repeat the Generate and Open a Detailed Plan by Running a Query section to generate another detailed plan.
See how it is faster…
As you can see, after creating the index, if we run the query again and view the detailed query plan generated from thefedtrace, we can see that the created indexL_SHIPDATEis being used. The type of index used here is the High Group (HG) index which is commonly used for join columns with integer data types. When we create the index, HANA is smart enough to coordinate and figure out which index would be the best choice. In this case, the query optimizer has determined that the HG index will be more effective than the FP index and chosen the HG index for the query execution.