Develop and Consume Queries on SAP Analytics Cloud
- How to create an analytical query as CDS View Entities
- How to connect an ABAP System to SAP Analytics Cloud
- How to consume analytical queries on SAP Analytics Cloud by creating models and stories
Prerequisites
- You need the standard developer authorization profile to create ABAP development objects.
- You need a SAP Analytics Cloud account.
- Install
ABAPGitPlugin in ADT. See http://eclipse.abapgit.org/updatesite/ - To get the Flight Model into the system, follow the description at https://github.com/SAP/abap-platform-refscen-flight/blob/master/README.md
- Requires Customer or Partner License.
Always replace #### with your initials or group number.
- Step 1
The new RAP based InA service exposure enables the SAP Business Technology Platform ABAP Environment developers to develop analytical queries(based on ABAP-CDS analytical data models) and expose them via the
InA(Information Access) service protocol. In this Tutorial you will create a complete Analytical Data Model for Booking data. This consists out of dimensions for Carrier, Customer, Connection and Agency data, as well as an interface CDS view for Booking data which acts as a data source for the cube and query.
These analytical queries can be further consumed in the SAP Analytics cloud to create analytical models, stories, multi-dimensional reports and more.
- Step 2
As a first task you will start to import templates that you will use in this tutorial to create Analytical CDS views such as dimension views, cubes and queries.
The templates already contain certain annotations that are mandatory for the above mentioned analytical CDS views. If values such as the name of a property have to be added this can then simply be done by using code completion.
-
Click on the following link to display the file analytical_templates.xml. Templates
-
Right-click on the browser window and save the content as an xml-file called analytical_templates.xml.

-
Open ADT. In the menu choose Window > Preferences.

-
In the Templates dialogue choose Import.

-
Select the XML file analytical_templates.xml that you have saved.

The Import-Dialog only allows to select files having the extension
.xml.When you have downloaded the file using a different file extension you have first to rename your file so that it gets the extension.xml. -
You will see that three new templates have been imported that you will use in the following tutorial.
Press Apply and Close

-
- Step 3
Dimensions views are links to various master data, which are later used in reporting as further attributes (according to which different aggregations can be made) and thus make up the versatility of our Analytical Model.
In the following you will create four dimension views for Carrier, Customers, Connections and Travel Agencies so that you can visualize our measures Number of bookings and Flight price in relation to these dimensions.
That means you will be able to create different charts that show how much money was spend for bookings for the connection Frankfurt–>New York compared to the connection Frankfurt–>Sydney or that show how much money was spend for flights with a certain airline.
You will start to create a dimension view that contains the different Airlines / Carriers. Since our model will contain two measures, namely Number of bookings and Flight Price you will be able to answer questions such as
- How much bookings are there per Carrier ? or
- How much money was spend for bookings for a certain Airline?
-
Open ADT and login to your ABAP System.
If you do not have a package, create a new one. -
Right-click your package and choose New > Other ABAP Repository Object.

-
Choose Core Data Services > Data Definition and click Next.

-
Enter the following values
- Name:
ZRAP500_I_CARRIER_### - Description:
Dimension for Carrier - Referenced Object:
/dmo/carrier
and click Next.
By selecting a table or another CDS view as Referenced object the wizard will use this object as a data source for the new CDS view and it will automatically add all fields into the DDL source code and it will also create camel Case aliases if needed.

- Name:
-
Choose a transport request and click Next.
Do NOT press Finish, because otherwise the wizard will not provide us the option to choose a specific template but would choose the template that you have used the last time.

-
In the Templates dialogue choose the Define a View Entity for a Dimension and press Finish. The Define a View Entity for a Dimension template is one of the new data definition templates that you have imported in the last step. This template contains certain annotations which will be explained below that are mandatory for dimension views.

- Step 4
-
Now you need to edit the dimension view. Here you can use code completion to add the values for the annotations
@ObjectModel.representativeKey
and
@ObjectModel.text.element
that are needed for our dimension view.

-
Click on
representativeKey, delete the placeholderrepresentativKeyso that you get an empty string ’’ , press CTRL + Space and chooseCarrierId.
-
Click on
textElement, delete the placeholder stringtextElement, press CTRL + Space and chooseName.
-
Save and activate the dimension.

-
Your final code should look like following:
ZRAP500_I_Carrier_####Copy
@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #CHECK @EndUserText.label: 'Dimension for Carrier' @Metadata.ignorePropagatedAnnotations: true @Analytics.dataCategory: #DIMENSION @Analytics.internalName: #LOCAL @ObjectModel.representativeKey: 'CarrierId' define view entity ZRAP500_I_Carrier_#### as select from /dmo/carrier { @ObjectModel.text.element: ['Name'] key carrier_id as CarrierId, name as Name, currency_code as CurrencyCode }Coding explained
Code Explanation @Metadata.ignorePropagatedAnnotations: true ignore annotations from tables and base views, because you want to completely control/override the annotations here. @Analytics.dataCategory you define this CDS view as a dimension. @Analytics.internalName: #LOCAL Create UUIDs. @ObjectModel.representativeKey: ‘CarrierId’ you define CarrierID as the representative key to be able to refer to it using @ObjectModel.foreignKey.association in the Cube that you will create later @ObjectModel.text.element: [‘Name’] Using this annotation you define that the attribute Name, contains the text element for a given CarrierId.
-
- Step 5
Customer Dimension
The data for customers is contained in the table
/dmo/customer. So you have to follow all steps above and create a dimensionZRAP500_I_Customer_####and use the table/DMO/customeras a data source / reference object.
The table/dmo/customercontains the columns first name and last name, but not the full name of the customer. You will hence add a new field to our CDS view where you calculate the full name so that you can use it as the text element for the key fieldCustomerId.
The table/dmo/customeralso contains fields that are too long to be used in analytics scenarios and it contains administrative fields that you do not want to show. You will hence delete these fields from the field list after having used the Define a View Entity for a Dimension template.-
Right click on your Core Data Services folder, choose Data Definition > New > Data Definition. Enter following values and press Next:
- Name:
ZRAP500_I_Customer_#### - Description:
Dimension for Customer - Referenced Object:
/dmo/customer

- Name:
-
Select a transport request and press Next
- Select again the template Define a View Entity for Dimension and press Finish
- Add a new field
CustomerNamewhich will later be specified as the text element for the key field.concat_with_space(first_name, last_name, 1) as CustomerName, -
Remove or comment out these fields because they are too long for our analytics scenarios and you do not need any administration fields.
// email_address as EmailAddress, // createdby as Createdby, // createdat as Createdat, // lastchangedby as Lastchangedby, // lastchangedat as Lastchangedat -
Add the association
_Countryassociation [1] to I_Country as _Country on $projection.CountryCode = _Country.Countryand add
_Countryto the field list so that it is exposed.

-
Choose the property
CustomerIdfor the annotation @ObjectModel.representativeKey and choose the newly created propertyCustomerNamefor the annotation @ObjectModel.text.element.
-
Save and activate the dimension.
You expose the association
_Countryto be able to access country information in the cube and query. -
Your final code should look like following:
ZRAP500_I_Customer_####Copy@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #CHECK @EndUserText.label: 'Dimension for Customer' @Metadata.ignorePropagatedAnnotations: true @Analytics.dataCategory: #DIMENSION @Analytics.internalName: #LOCAL @ObjectModel.representativeKey: 'CustomerId' define view entity ZRAP500_I_Customer_#### as select from /dmo/customer association [1] to I_Country as _Country on $projection.CountryCode = _Country.Country { @ObjectModel.text.element: ['CustomerName'] key customer_id as CustomerId, first_name as FirstName, last_name as LastName, concat_with_space(first_name, last_name, 1) as CustomerName, title as Title, street as Street, postal_code as PostalCode, city as City, country_code as CountryCode, phone_number as PhoneNumber, // email_address as EmailAddress, // createdby as Createdby, // createdat as Createdat, // lastchangedby as Lastchangedby, // lastchangedat as Lastchangedat _Country }
Connection Dimension
The information about the connections (flights) is stored in the table
/dmo/connection. In this dimension view you again add a new field. The newly created field Trip will show the departure airport and the destination airport in one string.
For tables such as/dmo/connectionthat contain more than one key field, the key fields that are not annotated as the representative key field have to be annotated with a foreign key relationship.
Since the key fieldConnectionIdwill be annotated as therepresentativeKeyyou have to add an association that points to the Carrier dimension view which will be added as a foreign key relationship to the key fieldCarrierId.- Right click on the folder Data Definitions > New > Data Definition.
- Enter the following values and press Next.
- Name:
ZRAP500_I_Connection_#### - Description:
Dimension for Connections - Referenced Object:
/dmo/connection
- Name:
-
Select a transport request and press Next.
- Select again the template Define a View Entity for Dimension and press Finish.
- Add a new field Trip which will later be specified as the text element for the key field
ConnectionId.concat(airport_from_id, concat(' -> ', airport_to_id)) as Trip, -
Add an association
_Carrierassociation [1] to ZRAP500_I_Carrier_#### as _Carrier on $projection.CarrierId = _Carrier.CarrierId
and expose it in the field list by adding
_Carrier -
Add the following annotation to the key field
CarrierId@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Carrier' -
Select the field
ConnectionIdfor the annotation@ObjectModel.representativeKey -
Select the field
Tripfor the annotation@ObjectModel.text.element -
Save and activate the dimension view.
-
Your final code should look like the following:
ZRAP500_I_Connection_####Copy@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #CHECK @EndUserText.label: 'Dimension for Connections' @Metadata.ignorePropagatedAnnotations: true @Analytics.dataCategory: #DIMENSION @Analytics.internalName: #LOCAL @ObjectModel.representativeKey: 'ConnectionId' define view entity ZRAP500_I_CONNECTION_#### as select from /dmo/connection association [1] to ZRAP500_I_Carrier_#### as _Carrier on $projection.CarrierId = _Carrier.CarrierId{ @ObjectModel.text.element: ['Trip'] @ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Carrier' key carrier_id as CarrierId, key connection_id as ConnectionId, airport_from_id as AirportFromId, airport_to_id as AirportToId, concat(airport_from_id, concat('->', airport_to_id)) as Trip, departure_time as DepartureTime, arrival_time as ArrivalTime, distance as Distance, distance_unit as DistanceUnit, _Carrier }
Agencies Dimension
The information about the Agencies that perform the bookings is stored in the table
/dmo/agencies.- Right click on the folder Data Definitions > New > Data Definition.
- Enter the following values and press Next
- Name:
ZRAP500_I_Agency_#### - Description:
Dimension for Agencies - Referenced Object:
/dmo/agency
- Name:
-
Select a transport request and press Next
- Select again the template Define a View Entity for Dimension and press Finish
- Remove these fields because they are too long for our analytics scenarios
// email_address as EmailAddress, // web_address as WebAddress -
Choose the property Name for the annotation @ObjectModel.text.element.
@ObjectModel.text.element: [‘Name’]
-
Choose the property
AgencyIdfor the annotation @ObjectModel.representativeKey.@ObjectModel.representativeKey: 'AgencyId' -
Save and activate the dimension view.
-
Your final code should look like the following:
ZRAP500_I_Agency_####Copy@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #CHECK @EndUserText.label: 'Dimension for Agency' @Metadata.ignorePropagatedAnnotations: true @Analytics.dataCategory: #DIMENSION @Analytics.internalName: #LOCAL @ObjectModel.representativeKey: 'AgencyId' define view entity ZRAP500_I_Agency_#### as select from /dmo/agency { @ObjectModel.text.element: ['Name'] key agency_id as AgencyId, name as Name, street as Street, postal_code as PostalCode, city as City, country_code as CountryCode, phone_number as PhoneNumber // , // email_address as EmailAddress, // web_address as WebAddress }
-
- Step 6
You now have to create an interface view that serves as a data source for the Cube.
-
Right click on the folder Data Definitions and choose New > New Data Definition from the context menu.
-
Enter the following values and press Next
- Name:
ZRAP500_I_Booking_#### - Description:
Interface View for Booking - Referenced Object:
/dmo/I_Booking_U

- Name:
-
Select a transport request and press Next.
Do NOT press finish at this point because you need to select a different template in the next step. - This time select the template Define a View Entity and then press Finish

-
Add an annotation
@Semantics.amount.currencyCodeto the property Flight Price that points to the propertyCurrencyCode.@Semantics.amount.currencyCode: ‘CurrencyCode’
-
Add a new field
AgencyId. The value for this field will be retrieved using the association_Travel.
That points to the parent entity. This way the fieldAgencyIdcan be used as a dimension field._Travel.AgencyID as AgencyID,

-
Save and activate the interface view.
-
Your final code should look like the following:
ZRAP500_I_Booking_####Copy@AbapCatalog.viewEnhancementCategory: [#NONE] @AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #CHECK @EndUserText.label: 'Interface View for Booking' @Metadata.ignorePropagatedAnnotations: true @ObjectModel.usageType:{ serviceQuality: #X, sizeCategory: #S, dataClass: #MIXED } define view entity ZRAP500_I_Booking_#### as select from /DMO/I_Booking_U { key TravelID, key BookingID, BookingDate, CustomerID, AirlineID, ConnectionID, FlightDate, @Semantics.amount.currencyCode: 'CurrencyCode' FlightPrice, CurrencyCode, _Travel.AgencyID as AgencyID, /* Associations */ _BookSupplement, _Carrier, _Connection, _Customer, _Travel }
-
- Step 7
The Cube is the analytical interface view that is ultimately used in the query and “holds together” the model. In addition to the facts and the measurable key figures (if necessary also calculations), it contains references to the dimensions.
You will now use the Booking interface view as a data source to create a cube. All cubes must have at least one measure. The measurable data are the quantifiable fields that can be calculated, such as number of flight bookings and price of a flight. Using a query, you can SUM these fields. To create a cube, there is a mandatory header annotation:
@Analytics.dataCategory: #CUBE
This annotation is part of the template Define a View Entity for a Cube that you have imported in your ADT installation at the beginning of this tutorial.
-
Right click Data Definition and choose New > New Data Definition.
-
Enter the following values and press Next
- Name:
ZRAP500_I_BookingCube_#### - Description:
Booking Cube - Referenced Object:
ZRAP_I_BOOKING_####(The booking interface view)

- Name:
-
Choose a transport request and then choose Define a View Entity for a Cube and click Finish.

-
Add the following associations
associationsCopyassociation [0..1] to ZRAP500_I_Customer_#### as _Customer on $projection.CustomerID = _Customer.CustomerId association [0..1] to ZRAP500_I_Carrier_#### as _Carrier on $projection.AirlineID = _Carrier.CarrierId association [0..1] to ZRAP500_I_Connection_#### as _Connection on $projection.AirlineID = _Connection.CarrierId and $projection.ConnectionId = _Connection.ConnectionId association [0..1] to ZRAP500_I_AGENCY_#### as _Agency on $projection.AgencyID = _Agency.AgencyIdyou also need to add the following to entries to the field list
_Agency, _Customer._Country as _CustomerCountry -
In the created cube you define
foreignKey associatonsvia_Customer,_Carrier,_Connection, and_Agencyto be able to fetch and expose information in the cube and in the query.- Add the annotation
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Customer'to the fieldCustomerId - Add the annotation
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Carrier'to the fieldAirlineID - Add the annotation
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Connection'to the fieldConnectionId - Add the annotation
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Agency'to the fieldAgencyID
- Add the annotation
-
Comment out both lines of annotation
@Semantics.amount.currencyCodeand the property Flight Price. -
Add the following two fields alongside with a foreign key association
foreignKeyCopy@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_CustomerCountry' _Customer.CountryCode as CustomerCountry, _Customer.City as CustomerCity, -
You add fields that contain information about the customers
customerCopy@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_CustomerCountry' _Customer.CountryCode as CustomerCountry, _Customer.City as CustomerCity, _Connection.Trip as Trip, -
You now add Measures to our cube.
You add a field
TotalOfBookingstotalOfBookingCopy@EndUserText.label: 'Total of Bookings' @Aggregation.default: #SUM 1 as TotalOfBookings,and the field Flight Price which is annotated as follows
Flight PriceCopy@Semantics.amount.currencyCode: 'CurrencyCode' @Aggregation.default: #MIN FlightPrice, -
Save and activate the cube.

-
Your final code should be look like following:
ZRAP500_I_BookingCube_####Copy@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #CHECK @EndUserText.label: 'Booking Cube' @Metadata.ignorePropagatedAnnotations: true @Analytics.dataCategory: #CUBE @Analytics.internalName: #LOCAL define view entity ZRAP500_I_BookingCube_#### as select from ZRAP500_I_Booking_#### association [0..1] to ZRAP500_I_Customer_#### as _Customer on $projection.CustomerID = _Customer.CustomerId association [0..1] to ZRAP500_I_Carrier_#### as _Carrier on $projection.AirlineID = _Carrier.CarrierId association [0..1] to ZRAP500_I_Connection_#### as _Connection on $projection.AirlineID = _Connection.CarrierId and $projection.ConnectionId = _Connection.ConnectionId association [0..1] to ZRAP500_I_Agency_#### as _Agency on $projection.AgencyID = _Agency.AgencyId { key TravelID, key BookingID, BookingDate, @ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Customer' CustomerID, @ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Carrier' AirlineID, @ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Connection' ConnectionID as ConnectionId, FlightDate, // @Semantics.amount.currencyCode: 'CurrencyCode' // FlightPrice, CurrencyCode, @ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Agency' AgencyID, @ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_CustomerCountry' _Customer.CountryCode as CustomerCountry, _Customer.City as CustomerCity, _Connection.Trip as Trip, /* Measures */ @EndUserText.label: 'Total of Bookings' @Aggregation.default: #SUM 1 as TotalOfBookings, @Semantics.amount.currencyCode: 'CurrencyCode' @Aggregation.default: #SUM FlightPrice, /* Associations */ _Carrier, _Connection, _Customer, _Travel, _Agency, _Customer._Country as _CustomerCountry }
-
- Step 8
Since a query belongs to the projection layer (formerly known as consumption layer) it must have a C in its name according to the naming convention used in the Virtual Data Model (VDM) used in SAP S/4HANA. To create a query, there is a mandatory header annotation: @Analytics.query: true
Again you can use a template that you have imported at the beginning of this tutorial.
-
Right click Data Definition and choose New Data Definition.
-
Enter the following values and press Next
- Name:
ZRAP500_C_BookingQuery_#### - Description:
Query for Booking - Referenced Object:
ZRAP500_I_BookingCube_####

- Name:
-
Choose a transport request and then press Next.
-
In the following dialogue choose Define a View Entity for Query and click Finish.

-
Edit the code of your query and add the annotation @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis to all properties except the two measures
FlightPriceandTotalOfBookings. All fields beside the fieldCustomerCountryget the annotation @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS, whereas the fieldCustomerCountrygets the annotation @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #COLUMN. -
You add a currency conversion to the field
FlightPriceto be able to comparison all flight prices in a single currency.``` @Semantics.amount.currencyCode: 'CurrencyCode' currency_conversion ( amount => FlightPrice, source_currency => CurrencyCode, target_currency => cast( 'EUR' as abap.cuky( 5 ) ) , exchange_rate_date => cast ('20200101' as abap.dats), exchange_rate_type => 'M' ) as FlightPrice ``` -
Save and activate the query.

Using the template the mandatory annotations for query is set automatically.
@Analytics.query: true
With the annotation @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis:, the elements of the view can be positioned on multiple axes: Rows, Columns and Free. The elements can be directly annotated with their axis. All measures (elements which can be aggregated) need to be on the same axis. The annotation of the first measure will therefore be used for all measures of the query. If @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: is not found, the system positions the measures on the columns. -
Your final code should look like the following:
ZRAP500_C_BOOKINGQUERY_####Copy@AccessControl.authorizationCheck: #CHECK @EndUserText.label: 'Query for Booking' @Analytics.query: true define view entity ZRAP500_C_BOOKINGQUERY_#### as select from ZRAP500_I_BookingCube_#### { @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS key TravelID, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS key BookingID, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS BookingDate, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS CustomerID, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS AirlineID, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS ConnectionId, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS FlightDate, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS CurrencyCode, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS AgencyID, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #COLUMNS CustomerCountry, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS CustomerCity, @AnalyticsDetails.query.axis: #ROWS Trip, TotalOfBookings, @Semantics.amount.currencyCode: 'CurrencyCode' currency_conversion ( amount => FlightPrice, source_currency => CurrencyCode, target_currency => cast( 'EUR' as abap.cuky( 5 ) ) , exchange_rate_date => cast ('20200101' as abap.dats), exchange_rate_type => 'M' ) as FlightPrice }
-
- Step 9
Similar to the SAP Fiori Elements preview which is offered for OData V2 UI and OData V4 UI service bindings there is now an Analytical Data Preview available. This can be used by the ABAP developer to test the implementation of an Analytical Query since the preview uses the InA protocol.
Now that you have created the query it is possible to use a data preview to test our implementation.
- Navigate to the folder Data Definition
- Right click on the query
ZRAP500_C_BOOKINGQUERY_####and select Open with > Data Preview

- A new browser tab will open and you might have to authenticate using the credentials of your SAP BTP ABAP environment system.

- You can see the data that has been retrieved using the InA-Protocol. Please note that the measures are grouped by the Country/Region Key.

- Step 10
You use a service definition to define which data is to be exposed as a business service, using one or more business service bindings.
-
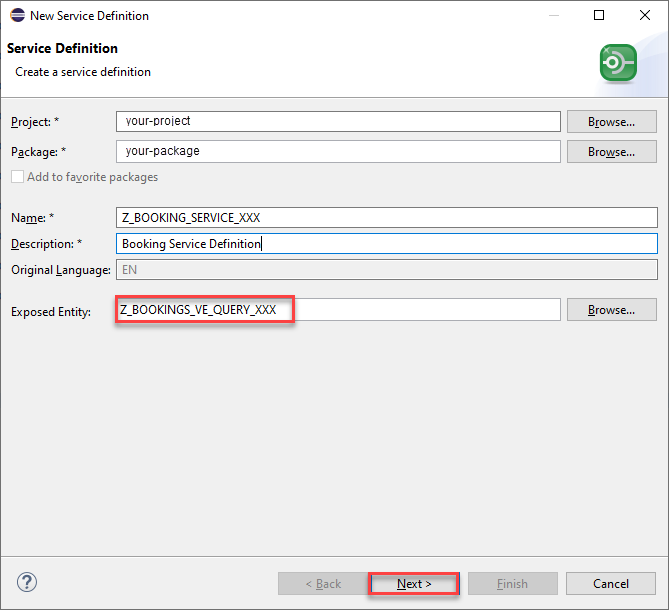
Right-click your created query in step 6 and choose New Service Definition.

-
Enter the following values and press Next.
- Name:
ZRAP500_UI_BOOKING_#### - Description:
Booking query service definition - check if Exposed Entity is your created query
ZRAP500_C_BOOKINGQUERY_####
- Name:
-
Select transport request and press Next.
- Select the template Define Service and press Finish.
- After the query is exposed as a service it must be activated by pressing Ctrl+F3
-
- Step 11
The service binding is used to bind a service definition to a communication protocol and in our case, the protocol that enables web-based data access from ABAP systems is the Information Access (InA) protocol.
-
Right click your newly created service definition and choose New Service Binding.
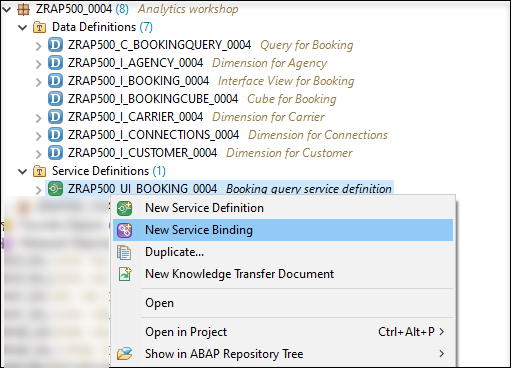
-
Enter the following values and press Next
- Name:
ZRAP500_UI_BOOKING_#### - Description:
Booking Query Service Binding - Choose InA - UI as Binding Type
- Check that in the field Service Definition the service definition
ZRAP500_UI_BOOKING_####is listed that you have created service definition in last step

- Name:
-
Choose a transport request and click Finish.
- Activate your service binding.
- After activation, the external service name for your query is displayed.

The analytical query will be displayed with the external service name in SAP Analytics Cloud as the data source.
-
- Step 12
-
Right-click your package, choose New > Other ABAP Repository Object.

-
Search for IAM App under Cloud Identity and Access Management. Click Next.

-
Enter the following values and press Next
- Name:
ZRAP500_BOOKING_#### - Description:
IAM App for Booking Query - choose EXT-External App as Application Type

- Name:
-
Choose a transport request and click Finish.
Your created IAM App name will get an EXT automatically in his name like:RAP500_BOOKING_####_EXT.
-
Go to the Services tab and click on insert button.

-
Select Service Type as
InA - UIand your Service Name which is your service binding nameZRAP500_UI_BOOKING_####. Click OK.
-
Save and Publish Locally.

-
- Step 13
-
Right-click Cloud Identity and Access Management in your package, choose New > Business Catalog.

-
Enter a Name and Description and click Next.

-
Choose a transport request and click Finish.
-
To create a Business Catalog App Assignment, in your created Business Catalog click Apps, click Add, assign your previously created external IAM app as IAM App. Enter a Name and Description and click Next.


-
Choose a transport request and click Finish. The Business Catalog App Assignment will be opened.
-
Back to the Business Catalog, choose your Assignment ID and click Publish Locally.

-
- Step 14
-
Login to the Fiori launchpad and open Maintain Business Roles App under Identity and Access Management.

-
Navigate to the
SAP_BR_DeveloperRole, select Assign Business Catalogs and click Edit.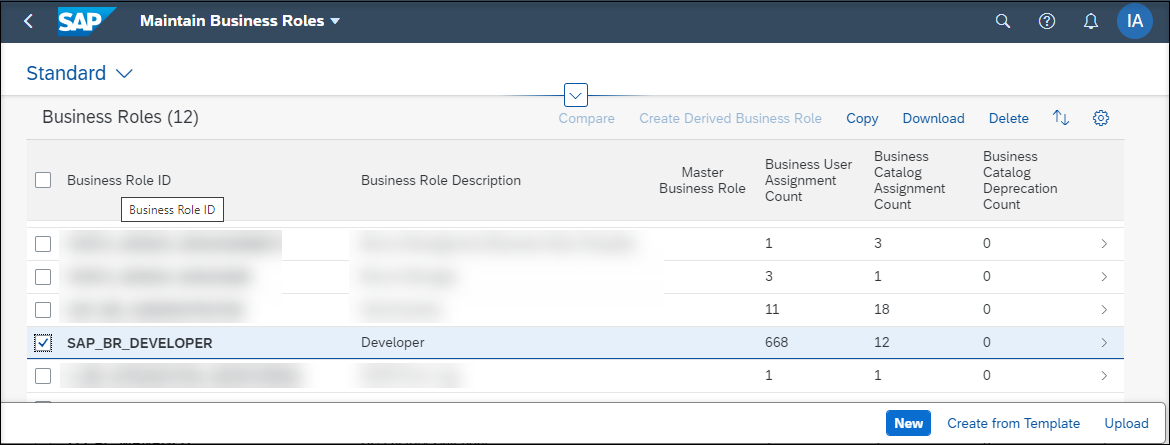

-
Click Add and find your business catalog in the popup and click OK to add the business catalog.


-
Check in the Assigned Business Catalogs, if your business catalog is added in the list. Click Save.

-
- Step 15
-
Back to the main page of Fiori launchpad and open Communication Systems App under Communication Management.

-
Click New to create a new communication system. Enter System ID and System Name, click Create.


-
The new communication system will be opened. Switch Destination Service to OFF and now enter you SAP Analytics Cloud host name (ex:
###.cloud.sap) as Host Name and443as Port. Click Save.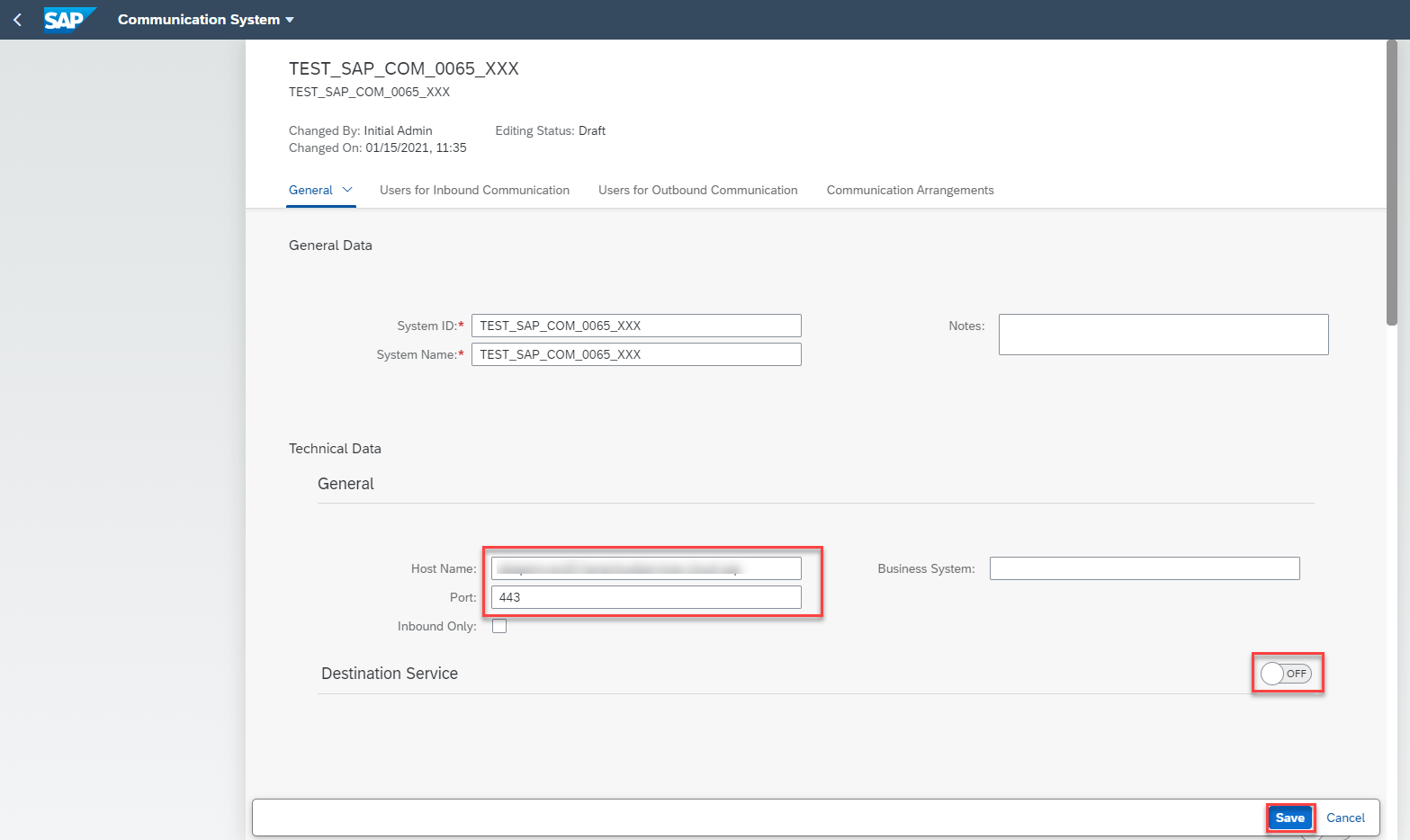
-
Back to the Communication Management and open Communication Arrangements to create a new one.

-
Click New and select
SAP_COM_0065as Scenario.Enter a name for your communication arrangement and click Create.
-
The new communication arrangement will be opened. Choose the communication system which you created previously in the Communication System field. Provide the Tenant ID of your SAP Analytics Cloud tenant.

Tenant ID can be found under the main menu of the SAP Analytics Cloud tenant, click System > About > System Name.
-
Under the Outbound Services, the service status for UI Link Navigation should be checked as Active and Retrieve Stories should be unchecked, click Save.

-
- Step 16
-
Login to the SAP Analytics Cloud tenant.

-
Open the main menu and click Connection and on the Connection Window click Add. In the popup under Connect to Live Data click SAP S/4 HANA.


-
In the New S/4 HANA Live Connection dialog enter Name and Description, Connection Type has to be Direct, for Host copy your Fiori launchpad link like
###.abap-web.stagingaws.hanavlab.ondemand.com. Enter443in HTTPS Port field, and100for Client. As Authentication Method choose SAML Single Sign-on (Standard Compliant). Click OK.
-
check the result.

-
- Step 17
Models transform your raw data into useful information that can then be used to create dynamic visualizations. Since you will use the unique feature Live Data Connection SAP Analytics cloud will create the model based on the analytical query that you have created and published in the previous exercise. Based on such a model you can perform online analysis without the need of data replication.
-
Expand navigation bar.

-
Choose Modeler and click Live Data Model

-
In the popup choose SAP BW for System Type

-
Choose your created connection in the last step as Connection and login with your username and password in the second popup.

-
Select your created Query in the last exercise as Data Source.

-
Click OK to continue.

-
In the model you can check all Dimensions and Measures.


-
Save the new model and enter the following values and click OK:
- Name:
ZRAP500_#### - Description:
Model ####

- Name:
-
Check your model in the Modeler page.

-
- Step 18
A story is a presentation-style document that uses various elements such as charts, images or tables to visualize your data.
Adding a chart starts with picking a chart type. Then you select your model and add measures and dimension and start on working how the data is displayed. Here you will create a story including a chart, a table and a Donut chart.Open a blank dashboard
-
Expand navigation bar and click Stories.

-
Choose Dashboard as your template.

-
A Blank Dashboard will be opened.

-
Enter a Dashboard Title like
RAP500_####.
Now you can insert some charts or tables and use the model you created before based on your analytical query.
Insert Chart
-
To insert a chart, click on the chart icon in the task menu and select your model with double clicking your model.
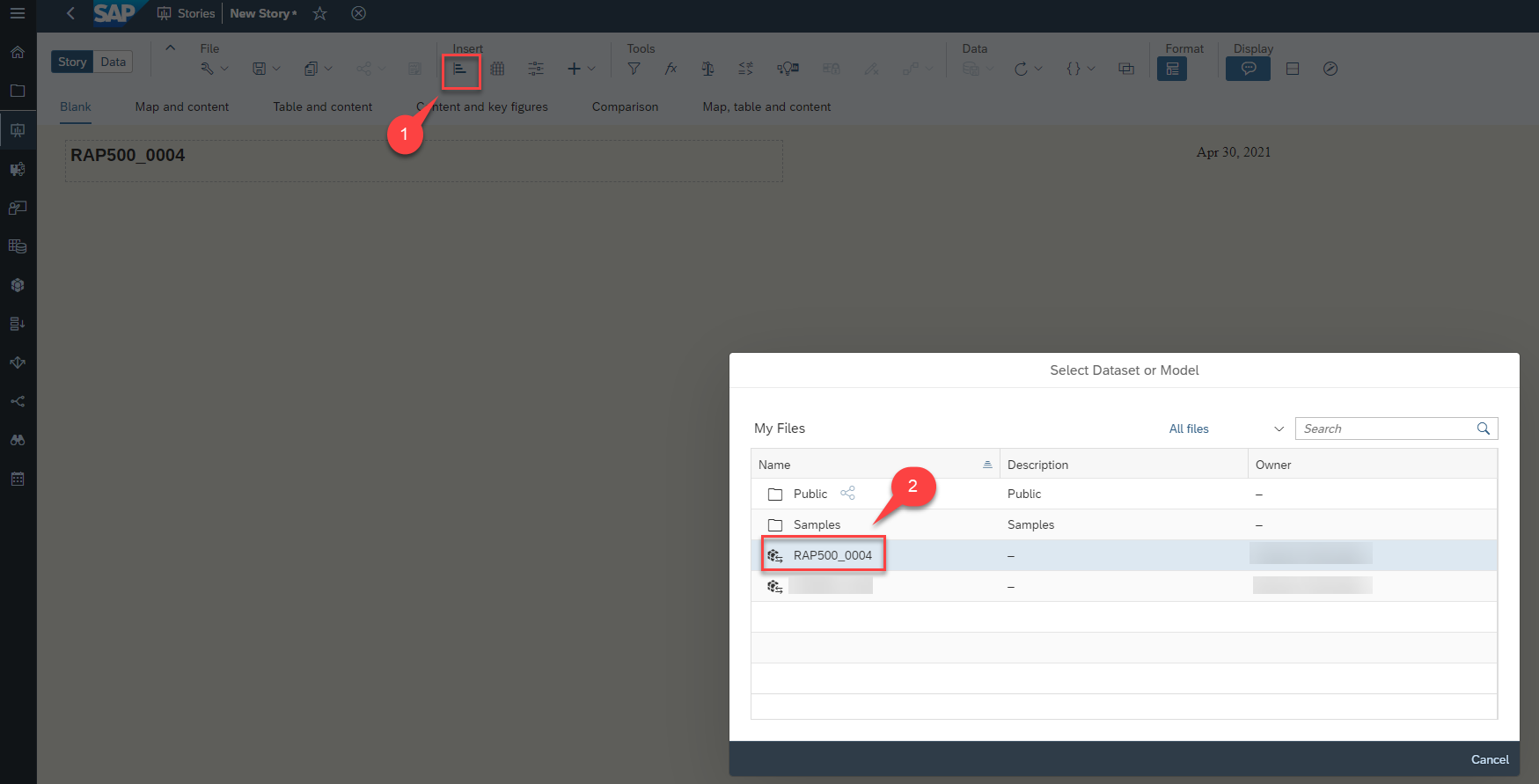
-
You can move the chart with click and drag around the page.

-
After you found a place for your chart, you need to add some measures and dimensions, which should be shown on the chart. You will find all settings on the right hand side under Builder.

-
Open + Add Measure and choose Flight Price. You will see the sum of all flight prices that have been booked on the chart.

-
Open + Add Dimension and choose Country/Region Key. Now there is a chart which shows how the flight costs are distributed in different countries your customers live in.

Insert Table
- To insert a table, click on the table icon. A Table will be created and all dimensions and measures will be displayed. You can move the table, make it bigger. You can change dimensions and measures under Builder.

In the table you can find all data from your query, what you choose as ROWS or COLUMNS. You have just one dimension
CustomerCountryin columns and all other dimensions are in rows.
Insert Donut Chart
-
Insert another chart and choose Donut under Builder > Chart Structure.

-
Choose Flight Price under + Add Measure and choose Airline ID under + Add Dimension.
You now have a visualization how the booking costs are distributed in different airlines.


Save the Story
-
You are almost done with your story, you need just to save the story. Click on save icon and choose Save.

-
Enter following values and click OK
- Name:
RAP500_####_Story - Description:
Story ###

- Name:
-
You will find your new created story under Welcome to Stories

You have used the preconfigured connection of the SAP Analytics Cloud instance to connect to the SAP BTP ABAP environment system where you have developed an Analytical Query. The data was retrieved using a Live Data Connection so that any change in the data was immediately reflected in the visualization of your query in SAP Analytics Cloud.
-
- Step 19
You can create more different and complicated analytics charts and tables with your query. Here there is some more examples.
-
Click the chart icon in the task menu, click Correlation and choose Scatter plot.

-
Choose Flight Price and Total of Booking as X and Y axis and Customer ID as dimension. You can choose Country/Region Key as Color dimension to have different colors for each country in this chart, you can make the chart bigger or move it around your dashboard too.

-
Click again chart icon in the task menu, click Distribution and choose Tree Map.

-
Choose Total of Booking as Size under Measures, TRIP as Label under Dimensions. You can change the title of the chart with double clicking the title or choose an other color for this chart.

-
Do not forget to save your story.

-
- Step 20
Where can you create a model or story?
- Overview
- Import templates for Analytical CDS views
- Create the first dimension for Carrier
- Edit dimension view
- Create three additional dimensions
- Booking interface view
- Create cube
- Implement query as CDS view entity
- Data preview
- Create service definition
- Create InA UI service binding
- Create IAM App
- Create business catalog
- Add business catalog to developer business role
- Create communication system and arrangement
- Connect the ABAP system to SAP Analytics Cloud
- Create model
- Create Story
- More analytics charts and tables
- Test yourself